Treating Underarm Pigmentation
Are you somebody that dreads wearing a sleeveless shirt, because you’re underarms are several shades darker than the rest of your body? Don’t worry, you’re not alone!
Many people suffer from dark underarms for a number of reasons. The appearance of dark underarms can be embarrassing at times and could also affect your self-confidence. We forget about taking care of our underarm skin. But this area can suffer from numerous problems such as pigmentation, ingrown hair, pimples, rashes, and rough bumpy skin.
Your underarms should naturally be about the same shade as the rest of your skin. But sometimes, the skin under the arms can turn darker. This is due to the rapid multiplication of pigment cells, which is medically known as Acanthosis Nigricans.
The causes of dark underarms – the science behind it

Carrying extra weight makes your body more resistant to the effects of insulin. This hormone helps regulate your blood sugar. High insulin levels in your blood can lead to increased production of skin pigment cells.
More than half of adults over 200 percent or more over their ideal body weight experience darkening in their underarms and other skin folds.

Obesity is also a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, a disease of high blood sugar. People who develop type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of Acanthosis Nigricans.

Some conditions that disrupt insulin levels can lead to Acanthosis Nigricans.
This includes:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): A common hormonal condition that affects women of reproductive age. It usually starts during adolescence, but symptoms may fluctuate over time.
- Cushing syndrome: A hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high cortisol levels, a hormone the adrenal glands produces.
- Acromegaly: A rare disorder in adults in which the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone.
- Hypothyroidism: A condition in which the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone.

Certain medications increase your insulin levels, which can lead to underarm darkening.
This includes:
- Insulin
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone
- Human growth hormone
- Birth control pills

In rare cases, sudden skin darkening could be a sign of cancer. When this happens, it often affects the stomach, liver, or colon. These tumors increase levels of growth factors that stimulate skin pigment cells.
When acanthosis nigricans is caused by cancer, it’s called malignant acanthosis nigricans. You’ll likely see dark patches around your mouth.

Acanthosis Nigricans appears to run through families so you can become its victim genetically.
treatment
Treating the medical condition that caused your dark underarms will often fix the issue. A combination of treatment products and procedures home could help lighten the color.
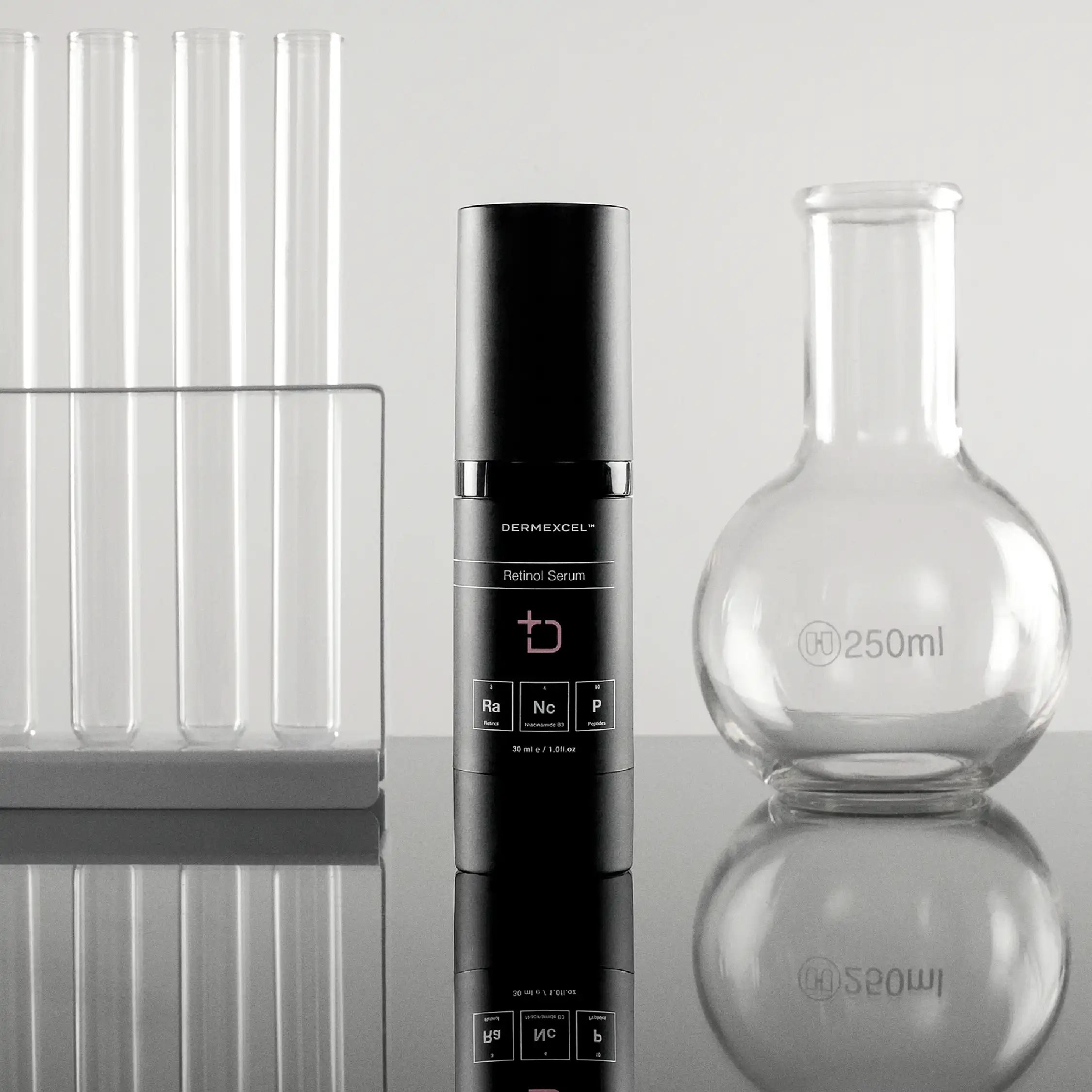
- Retinol is considered the first-line treatment for acanthosis nigricans. When used regularly, it can help thin and lighten the skin in affected areas. Dermal Health Science recommends DermExcel Retinol serum
- Chemical Exfoliators help to remove the thicker, damaged skin to reveal new, smooth skin. Dermal Health Science recommends DermExcel Chemical peel spray.
DermExcel Treatment
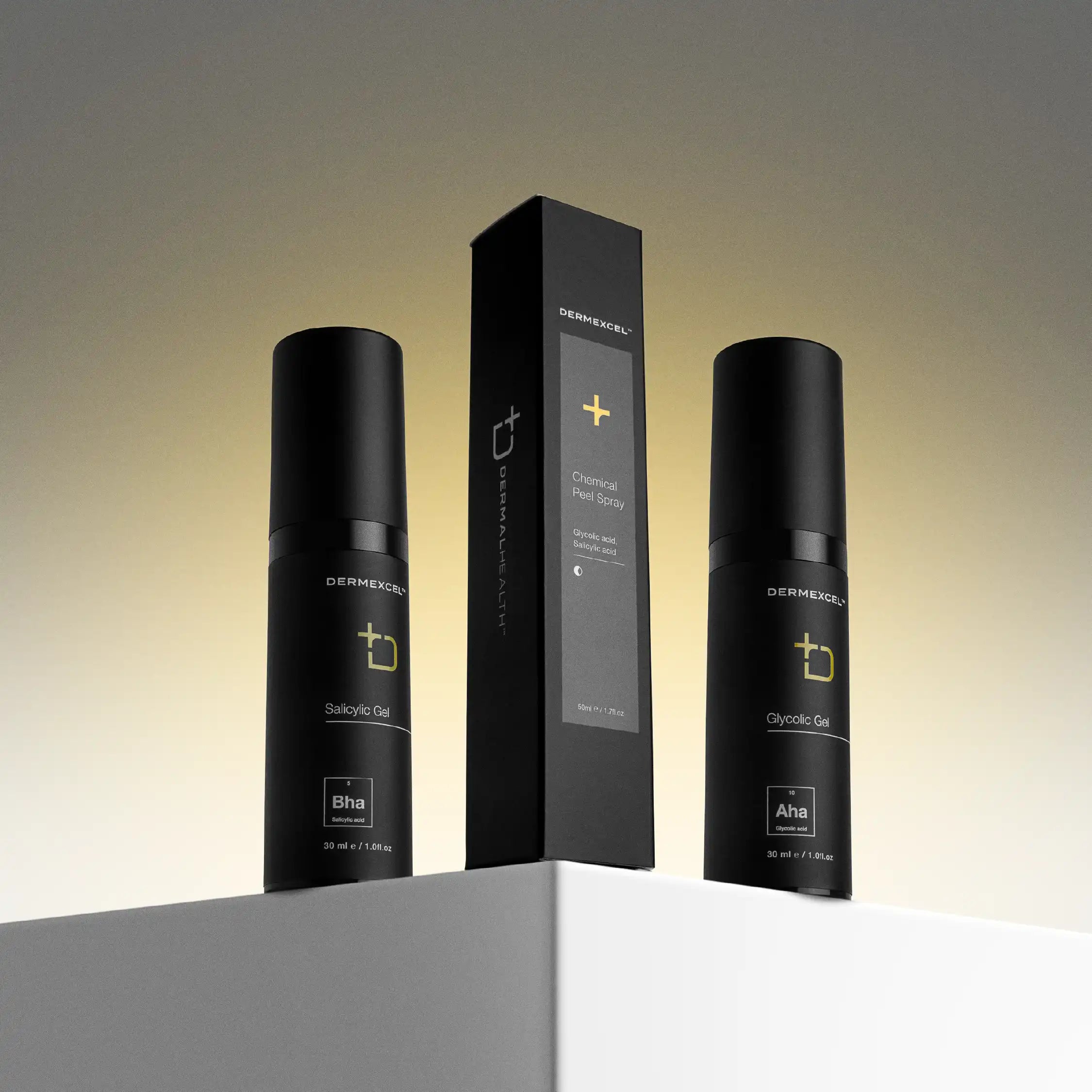






Dual-Action Exfoliator
Pay interest-free installments from R 193.00 with various payment gateways selected at checkout.
SIZE: 50 mL

Exfoliating

Smooth Skin

Ingrown hair

Anti-Acne

Anti-Aging
A scientifically-formulated solution, leveraging the synergistic effects of 10% Glycolic acid and 3% Salicylic acid. These active ingredients are renowned in the medical and pharmaceutical fields for their potent anti-aging and anti-acne properties.
Salicylic acid, a beta hydroxy acid, deeply penetrates pores, effectively targeting pimples, blackheads, Keratosis Pilaris, and ingrown hair bumps. It works by dissolving excess sebum and dead skin cells, thereby preventing pore clogging.
Glycolic acid, an alpha hydroxy acid, stimulates cellular turnover, aiding in the reduction of pigmentation and enhancing collagen production, which is crucial for maintaining skin elasticity and reducing signs of aging.
The product is designed as a lightweight liquid that dries rapidly on the skin, eliminating concerns about staining fabrics. This makes it a practical and efficient solution for combating body acne, including on the back and buttocks, and for promoting overall skin health.
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid, a renowned beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is a cornerstone in dermatology and skincare due to its exceptional keratolytic and comedolytic properties. Its unique ability to penetrate oil-laden hair follicle pores makes it particularly effective in treating acne-prone and oily skin types.
Salicylic acid dissolves skin debris (sebum and dead skin cells) that clogs pores and causes acne. It's a mild antibacterial and powerful anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the redness and swelling associated with breakouts.
What sets salicylic acid apart in dermatological treatments is its ability to exfoliate the skin, not just on the surface but within the pores themselves. This is due to its oil-soluble nature, which allows it to penetrate deep into the pores and dissolve the keratin plugs that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
Furthermore, salicylic acid also has the capacity to adjust the pH of the skin, creating an environment less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Salicylic acid's efficacy in treating various skin conditions, particularly acne, has been extensively documented in the scientific literature. Studies have consistently shown its ability to reduce acne lesions in terms of count and severity. Additionally, salicylic acid is highly recommended for its effectiveness in treating other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and dandruff, due to its ability to soften and remove scales and flakes from the skin.
Physiological Effects
- Keratolytic Action: Salicylic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin by dissolving the intercellular 'glue' that holds skin cells together, helping to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Comedolytic Effect: It is particularly effective in reducing comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by unclogging pores and preventing the formation of new comedones.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Salicylic acid reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps to regulate oil production, making it a valuable ingredient for managing oily and acne-prone skin.
- Penetration Enhancement: Due to its lipophilic nature, it can penetrate sebum-filled follicles, effectively treating acne located deep within the pores.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Vulgaris: Salicylic acid is a cornerstone in acne treatment, effectively preventing and treating existing acne lesions.
- Psoriasis: Its keratolytic properties make it helpful in softening and removing scales associated with psoriasis.
- Warts: Salicylic acid is commonly used to treat warts because it can exfoliate and remove thick skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: It helps manage seborrheic dermatitis by reducing scaling and redness.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Salicylic acid can aid in smoothing the rough bumps associated with peratosis Pilaris.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 3, 135.
- Zander, E., & Weisman, S. (1992). Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics.
- Gupta, A. K., & Nicol, K. (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.






Pay interest-free installments from R 335.00 with various payment gateways selected at checkout.
SIZE: 30 mL

Unclog Pores

Minimize Pores

Smooth Skin

anti-aging

DNA repair
A scientifically formulated skincare solution with state-of-the-art active ingredients. Retinol Serum stimulates epidermal growth and counters signs of aging, reducing hyperpigmentation and promoting collagen and elastin growth, vital for skin elasticity and structure.
Retinol Serum supports skin cell health, protecting skin cells from environmental stressors and aiding acne treatment. Its advanced formulation stimulates collagen production, reduces inflammation, inhibits pigmentation, and accelerates cell turnover. It also aids in combating acne by reducing sebum production and unclogging pores.
Retinoic acid analogue
Retinoic acid, often referred to as tretinoin in its pharmaceutical form, is the active form of Vitamin A. It is widely recognized for its powerful effects in dermatology and skin care, particularly in treating acne and signs of skin aging.
Retinoic acid works at the cellular level to modify gene expression and affect cell growth. In treating acne, it promotes the turnover of skin cells, reducing the likelihood of pore-clogging and helping to clear existing breakouts. Additionally, it decreases the cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells, further preventing the formation of comedones.
Retinoic acid's ability to stimulate collagen production is a key benefit in anti-aging skincare. This leads to a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles and an improvement in overall skin texture and tone. It also aids skin discoloration and hyperpigmentation by accelerating cell turnover, bringing new skin cells to the surface faster, and shedding pigmented and damaged cells.
Despite its benefits, retinoic acid can irritate the skin, causing side effects like redness, dryness, and peeling, especially during the initial period of use. Its potency means it is generally available by prescription and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is a newer, esterified form of retinoic acid. Unlike cosmetic retinol, HPR binds directly to the retinoid receptors of the skin cells without needing conversion. This direct binding allows it to deliver similar benefits to retinoic acid, such as stimulating collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and reducing signs of aging, but with a lower risk of irritation.
HPR is considered more gentle and less irritating than traditional retinoic acid while offering comparable benefits. With HPR, everyone has access to the benefits of prescription retinoids without the risk of side effects.
Physiological Effects
- Cell Turnover and Renewal: HPR promotes rapid cell turnover, aiding in the exfoliation of dead skin cells and generating new cells.
- Skin Texture: Promoting cell renewal improves skin texture and addresses issues like roughness and dullness.
- Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improving skin elasticity.
- Acne Treatment: Effective in treating acne by unclogging pores and reducing the size of sebaceous glands, it diminishes both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions.
- Pigmentation: It can reduce hyperpigmentation by accelerating the turnover of hyperpigmented skin cells and inhibiting melanin production.
- Photoaging: Effective in treating signs of photoaging, reversing some of the damage caused by UV radiation.
Special Benefits
- Retinoid Receptor Activity: HPR, an ester of retinoic acid, binds directly to retinoid receptors in the skin, enabling it to work without needing to be converted into retinoic acid.
- Lower Irritation: Typically, it causes less irritation than retinoic acid, making it more suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Collagen Stimulation and Anti-Aging: Like retinoic acid, HPR helps in stimulating collagen production and has anti-aging properties.
- Acne and Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats acne and reduces hyperpigmentation, often with fewer side effects than retinoic acid.
- Stability and Penetration: HPR is more stable and lipid-soluble, so it penetrates the skin more effectively and is less prone to degradation.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., ... & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Fisher, G. J., Wang, Z. Q., Datta, S. C., Varani, J., Kang, S., & Voorhees, J. J. (1996). Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. New England Journal of Medicine, 337(20), 1419-1428.
- Truchuelo, M. T., Jiménez, N., Jaén, P. (2018). Assessment of the efficacy of a new complex-based retinoic acid and retinol in a 3-month study using objective methods and skin biomarker analysis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 17(3), 347-354.
- Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging.
- Randhawa, M., et al. (2015). Hydroxypinacolone retinoate: a new retinoid and its use in dermatology. Skin Therapy Letter.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids with a wide range of biological functions and skin benefits. They are essentially small fragments of proteins, which are fundamental components of all living cells, including collagen and elastin in the skin.
In skincare, peptides are known for enhancing skin repair and rejuvenation. They function as signaling molecules, instructing cells to perform specific tasks such as producing collagen and elastin, vital for maintaining the skin's firmness and elasticity. This makes peptides especially beneficial in anti-aging products, as they can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Research has shown that certain peptides can improve skin barrier function, increase hydration, and soothe skin inflammation. This makes them suitable for products targeting dry, sensitive, or inflamed skin.
Peptides, with their diverse functions in promoting collagen production, strengthening the skin barrier, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory actions, are pivotal in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly in anti-aging, sensitive skin care, and wound healing applications.
Physiological Effects
- Collagen Production: Certain peptides, known as signal peptides, stimulate collagen production in the skin, enhancing skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Barrier Strengthening: Peptides can strengthen the skin barrier, improve hydration, and protect against environmental damage.
- Wound Healing: Some peptides play a role in the skin's natural healing process, aiding tissue repair and regeneration.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Certain peptides have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to soothe and calm irritated skin.
- Antimicrobial Action: Some peptides possess antimicrobial properties, potentially helping to manage acne and other skin infections.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Peptides can stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity.
- Sensitive Skin Conditions: Peptides are beneficial for sensitive or inflamed skin due to their soothing properties.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Antimicrobial peptides can be effective in acne treatment formulations.
- Wound Care and Repair: Peptides improve wound healing and reduce scarring.
References
- Gorouhi, F., & Maibach, H. I. (2009). Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Schagen, S. K. (2012). Topical peptide treatments with effective anti-aging results. Cosmetics.
- Varani, J., et al. (2001). Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Matrixyl 3000
Matrixyl 3000: The Powerhouse of Anti-Aging Peptides
Matrixyl 3000, a trademarked peptide composition, has revolutionized the approach towards anti-aging in dermatological products. This innovative ingredient combines two peptides, Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 and Palmitoyl Tetrapeptide-7. The synergy of these peptides enhances skin repair and reduces the appearance of aging.
Physiological Effects
- Collagen and Elastin Stimulation: Matrixyl 3000 promotes the production of collagen and elastin, key proteins that provide skin structure and elasticity. This helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Repair and Regeneration: It aids in the skin's repair process, enhancing the overall texture and tone, and may help reverse the signs of aging.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Matrixyl 3000 can have anti-inflammatory effects, reducing inflammation and potentially aiding in skin repair.
- Hydration Enhancement: Improving the underlying skin structure can enhance hydration, leading to a plumper, more youthful appearance.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its primary use is in anti-aging skincare products to combat wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of aging.
- Improving Skin Texture and Tone: Matrixyl 3000 can improve overall skin texture, which is beneficial for skin that has lost smoothness or become rough due to aging.
- Skin Elasticity: It can help improve skin elasticity, making it appear firmer and more toned.
Biochemical Mechanism and Clinical Efficacy
Matrixyl 3000 mimics the appearance of broken-down collagen, causing the skin to react by producing more collagen and elastin. Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 is known for stimulating collagen synthesis and firming the skin, while Palmitoyl Tetrapeptide-7 reduces inflammation, a key contributor to aging.
Studies have shown that Matrixyl 3000 significantly improves skin elasticity and reduces wrinkle depth. A notable study published in the "International Journal of Cosmetic Science" demonstrated that Matrixyl 3000 reduced wrinkle volume and depth by up to 45% after 2 months of use (Smith, 2005).
Matrixyl 3000 stands out as a non-irritating, highly effective ingredient. Its role in stimulating collagen and elastin production and reducing inflammation is a cornerstone in anti-aging skincare regimens.
References
- Smith, J. (2005). "Effects of Matrixyl 3000 on Skin Aging." International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Sederma Inc., "Matrixyl 3000 Technical Overview."
- Blackburn, R. S., et al. (2005). Matrixyl 3000 restores skin's metabolic balance. Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Lintner, K., et al. (2007). Matrixyl 3000: A new approach to anti-aging. Personal Care Magazine.
- Gorouhi, F., & Maibach, H. I. (2009). Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8: The Innovative Peptide in Anti-Aging Dermatology
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 is a testament to the advancements in peptide technology in dermatology. Its ability to reduce facial muscle contractions non-invasively positions it as an essential ingredient in anti-aging skincare.
Biochemical Mechanism
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 functions by inhibiting the neurotransmitters that trigger muscle contractions. This action reduces the intensity of wrinkle-causing facial expressions, leading to a visible decrease in fine lines and wrinkles. It mimics the N-terminal end of SNAP-25, competing with this natural protein for a position in the SNARE complex, thereby destabilizing it. As a result, neurotransmitter release is diminished, and facial muscle contractions are softened.
Physiological Effects
- Neurotransmitter Inhibition: Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 works by inhibiting neurotransmitter release. This leads to reduced facial muscle contraction, a mechanism similar to Botox but less invasive.
- Reduction of Expression Lines: Helps to reduce the appearance of expression lines, particularly around the forehead and eyes, by limiting muscle contraction.
- Improvement in Skin Texture: Regular use can lead to smoother skin texture and a reduction in the depth and severity of wrinkles.
Special Benefits
Clinical Efficacy - Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 in reducing wrinkle depth. A study published in the "International Journal of Cosmetic Science" reported that a cream containing 10% Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 reduced wrinkles by 30% over 30 days (Blanes-Mira et al., 2002).
References
- Blanes-Mira, C., et al. (2002). A synthetic hexapeptide (Argireline) with antiwrinkle activity. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Wang, Y., et al. (2013). The anti-wrinkle efficacy of Argireline. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy.
- Ruiz, M. A., et al. (2007). New cosmetic formulations containing Argireline. Journal of Cosmetic Science.







Keratolytic Treatment
Pay interest-free installments from R 83.00 with various payment gateways selected at checkout.

Ingrown hair

Body Acne

Keratosis Pilaris

Rough Skin

cracked heels
A clinically-formulated ointment to treat calloused, rough, and dry skin. It's more than a standard moisturizer; it exfoliates dead skin cells and replenishes moisture. The product creates an optimal environment for skin health, leading to a smoother complexion. Key ingredients include 10% Glycolic acid for exfoliation, 10% Lactic acid for removing dead cells, and 20% Urea for lasting hydration. Its "cream-ointment" base balances efficacy and application comfort. Dermalytic's medical-grade formula and scientific skincare approach visibly improve skin texture, giving users a renewed sense of confidence and comfort.
Note: Dermalytic is too potent for facial use.
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Urea
Urea, a naturally occurring compound in the skin, is widely recognized in dermatology and skin care for its hydrating and keratolytic properties. It is a component of the skin's natural moisturizing factor (NMF) and is crucial in maintaining skin hydration and barrier function.
In skin care, urea is valued for its dual action: it acts as a humectant, drawing moisture into the skin, and as a keratolytic agent, helping to break down the protein bonds between dead skin cells, leading to smoother and softer skin. This makes it particularly effective in treating dry, rough, and scaly skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and ichthyosis.
Additionally, urea has been shown to have antimicrobial properties and can aid in skin barrier repair, further underscoring its utility in treating various skin conditions.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Urea is a potent humectant, meaning it draws moisture into the skin, significantly improving hydration and maintaining skin moisture balance.
- Keratolytic Action: Urea has keratolytic properties, helping to break down the bonds between dead skin cells and aiding in the exfoliation of the skin's surface.
- Skin Barrier Function: Urea enhances the skin's barrier function, helping to prevent moisture loss and protect the skin from external irritants.
- Soothing Effect: It soothes dry, itchy, and irritated skin, providing relief from various skin conditions.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Urea is a key ingredient in many moisturizers for treating dry skin due to its excellent hydrating properties.
- Eczema and Psoriasis: It helps manage symptoms like dryness, scaling, and itching in eczema and psoriasis.
- Ichthyosis and Keratosis Pilaris: The keratolytic action of urea makes it effective in conditions characterized by excessive skin scaling, such as ichthyosis and keratosis pilaris.
- Cracked Heels and Calluses: Urea-based creams effectively soften and reduce thickened skin on heels and calluses.
- Aging Skin: It can improve skin texture and hydration in aging skin.
References
- Lodén, M. (2003). Role of topical emollients and moisturizers in the treatment of dry skin barrier disorders. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Pan, M., et al. (2013). Efficacy of topical urea in the treatment of xerosis. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Fluhr, J. W., et al. (2008). Glycerol and the skin: holistic approach to its origin and functions. British Journal of Dermatology.
- Grether-Beck, S., Felsner, I., Brenden, H., Kohne, Z., Majora, M., Marini, A., ... & Krutmann, J. (2012). Urea uptake enhances barrier function and antimicrobial defense in humans by regulating epidermal gene expression. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 132(6), 1561-1572.
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, a member of the alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) family, is a well-regarded ingredient in the field of dermatology and skincare for its exfoliating and moisturizing properties. Naturally occurring in sour milk and other fermented products, lactic acid is also produced in the human body and plays a role in various metabolic processes.
In skincare, lactic acid is primarily known for its ability to exfoliate the skin gently. By breaking down the bonds that hold dead skin cells together on the skin's surface, lactic acid helps to promote the shedding of these cells, revealing fresher, brighter skin underneath. This exfoliation process improves skin texture and tone and stimulates cell renewal.
One key advantage of lactic acid over other AHAs is its moisturizing capability. Lactic acid helps increase the skin's natural moisturizing factors (NMF), essential for keeping the skin hydrated. Its unique ability to draw moisture into the skin is particularly beneficial for treating dry and dehydrated skin conditions.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: A gentle exfoliant that removes dead skin cells from the skin's surface, promoting smooth skin.
- Moisture Retention: It is a humectant that helps the skin retain moisture, improving hydration and reducing dryness.
- Collagen Stimulation: Lactic acid can stimulate collagen production in the deeper layers of the skin, aiding in skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Brightening: It helps lighten dark spots and even out skin tone, effectively treating hyperpigmentation.
- pH Balancing: Lactic acid can help balance the skin's natural pH levels, which is beneficial for maintaining a healthy skin barrier.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Lactic acid's collagen-stimulating and exfoliating properties make it effective in anti-aging treatments, reducing signs of aging like wrinkles and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: By unclogging pores and removing dead skin cells, lactic acid can help reduce acne breakouts.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Its humectant properties are beneficial in hydrating and relieving dry skin.
- Hyperpigmentation: Lactic acid treats hyperpigmentation issues, including melasma and sun damage.
- Keratosis Pilaris: It can help manage keratosis pilaris by exfoliating the excess keratin that blocks hair follicles.
References
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Stiller, M. J., et al. (1996). Topical 8% glycolic acid and 8% L-lactic acid creams for the treatment of photodamaged skin. A double-blind vehicle-controlled clinical trial. Archives of Dermatology.
- Rawlings, A. V., Davies, A., Carlomusto, M., Pillai, S., Zhang, K., Kosturko, R., ... & Watson, D. (1996). Effect of lactic acid isomers on keratinocyte ceramide synthesis, stratum corneum lipid levels and stratum corneum barrier function. Archives of Dermatological Research, 288(7), 383-390.