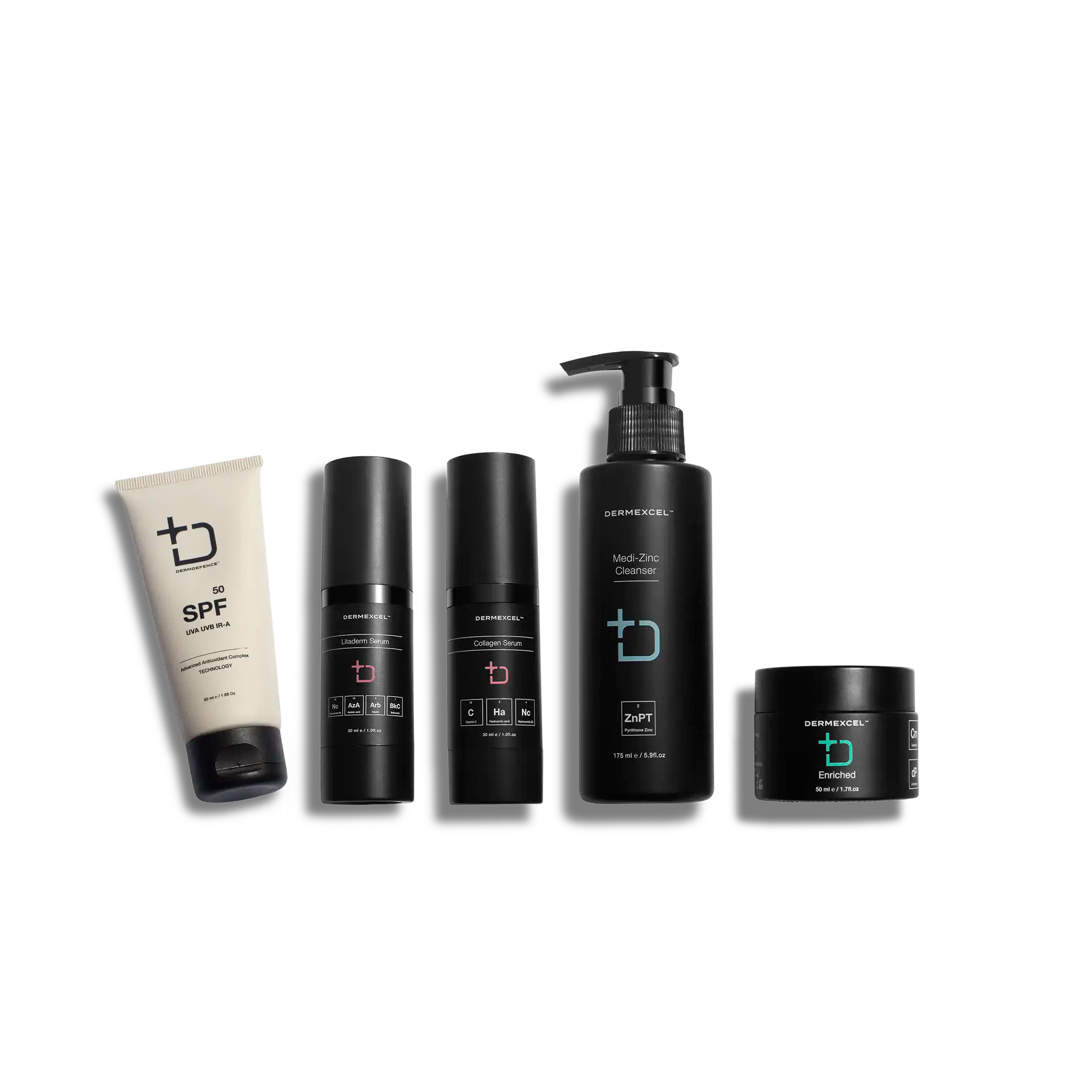
Treatment pack for Dermal Diagnosis: Aging.Dry.Pigmentation.Allergy during pregnancy

barrier repair

↓ inflammation

Anti-Aging

Skin Smoothing

Moisturizing
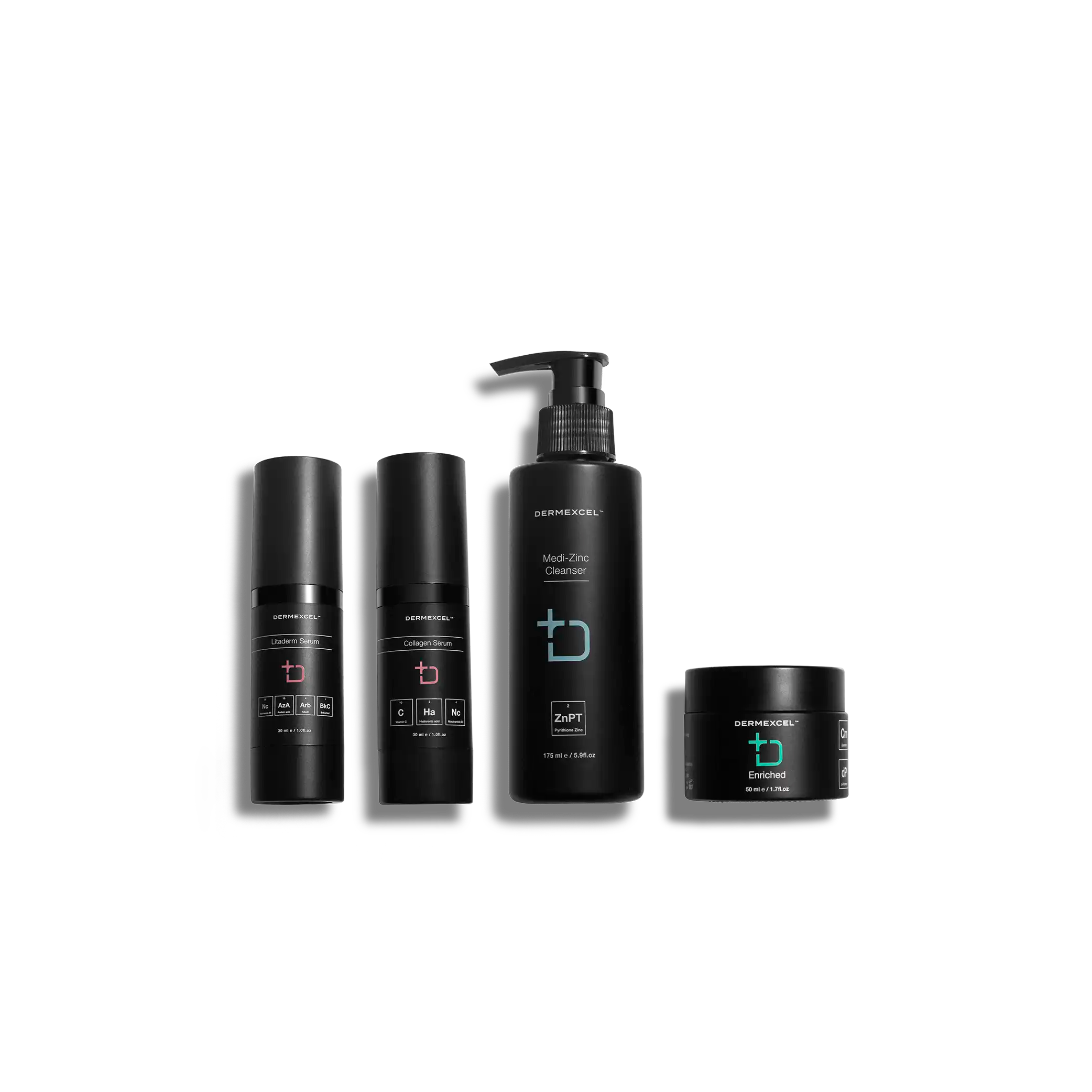
Products included
Free Gift with your treatment pack

Cotton Bag




SHIPPING
- Shipping Guarantee: Guiding you to healthy skin isn’t only about our products; it's also about getting them to you as swiftly as the science behind them. That's why Dermal Health offers a shipping guarantee you can rely on.
- Where We Ship From: Orders are dispatched from our facilities in Pretoria.
- Who We Ship With: We trust only well-known, popular, and dependable courier services with your packages.
- When You'll Get It: Expect confident skin soon! Shipping addresses in Pretoria and Johannesburg will enjoy delivery from same-day to 2 business days. Shipping addresses further from Pretoria may expect delivery within 1-4 business days, depending on the service you select during checkout. Your estimated delivery date will reflect during checkout so that you can mark your calendar.
- Tracking Your Order: Eager to start your DermExcel journey? We don't blame you! You'll receive a tracking number after you place your order so that you can follow your package.
For any shipping inquiries, our customer service team is ready to assist.
RETURNS
We are passionate about guiding you to healthier skin through medical science. We believe in the quality and proven effectiveness of our formulations — and we’re committed to supporting you on your journey to real, visible results.
That’s why we offer a 30-Day Confidence Guarantee. If, after consistent use as directed, you genuinely feel that your skin has not improved in any meaningful way — and you can demonstrate this (for example, with before-and-after photos or a brief description of your experience) — you’re welcome to request a return within 30 days of receiving your order, in line with our return policy.
Healthy skin is not complicated — and neither is our return process. To view the full terms, please visit our detailed return policy or contact our friendly customer care team. We’re here to help.
Feel as confident in us as we want you to feel in your skin.
SECURE PAYMENT
Dermal Health Science 30-Day Confidence Guarantee: We are passionate about guiding you to healthy skin through medical science. We believe in the quality and effectiveness of our products so much that we offer a 30-Day Confidence Guarantee.
If you're unsatisfied with your purchase, simply return it within 30 days for a full refund.
Healthy Skin Is Not Complicated and neither is our return policy. Please visit our detailed return policy or contact our friendly customer service team for more information.
Feel as confident in us as we want you to feel in your skin.

Choose options



Treatment pack for Dermal Diagnosis: Aging.Dry.Pigmentation.Allergy during pregnancy
MORNING
EVENING
MORNING
EVENING
Morning Regimen Notes
For the best use of Medi-Zinc Cleanser, please check the detailed instructions on its product page. You can access this page by clicking the cleanser's name above.
Apply Collagen Serum to damp skin every morning after cleansing.
If your skin feels dry in the mornings after you apply your serum: wait a few minutes, and then layer it with Enriched.
After you apply your serum or moisturizer, wait a few minutes, then layer with Dermdefence SPF 50.
- After you apply Collagen Serum, wait a few minutes, then layer with Litaderm Serum.
- After you apply Litaderm Serum, wait a few minutes, then layer with Dermdefence SPF 50.
- You should not follow the intensified treatment regimen if you have very sensitive skin.
Evening Regimen Notes
For the best use of Medi-Zinc Cleanser, please check the detailed instructions on its product page. You can access this page by clicking the cleanser's name above.
Apply Litaderm Serum to damp skin every evening after cleansing.
If you have sensitive skin, use Litaderm Serum only 2-3 times per week.
After you apply your serum, wait a few minutes then layer with Enriched.
Important Notes
- Reduce Litaderm Serum application frequency to 2-3 times per week and apply Enriched instead.
- After irritation subsides, slowly increase the frequency of use as tolerated by your skin.
Medi-Zinc Cleanser - 100ml / 175ml
(Depending on the size you selected)Dermdefence SPF 50
(Based on your selection)This regimen is designed for skin affected by aging, dryness, pigmentation, and allergy-prone sensitivity often associated with atopic dermatitis during pregnancy. It focuses on restoring hydration, reinforcing the skin barrier, and calming inflammation while addressing uneven tone. Key ingredients such as Ceramides, Hyaluronic acid, Niacinamide, and soothing anti-inflammatory agents help reduce flare-ups, improve skin texture, and support a more resilient, even-toned complexion throughout pregnancy-related changes.
your frustrations
- Impaired and dehydrated skin barrier.
- Visible signs of skin aging.
- Rough skin texture.
- Sensitive skin that reacts to various stimuli and products.
- Skin prone to allergic reactions.
- Uneven skin tone with dark spots or patches.
your goals
- Restore hydration and moisture.
- Strengthen skin barrier.
- Smooth skin texture.
- Reduce and prevent visible signs of skin aging.
- No allergic skin reactions.
- Radiant skin with an even skin tone.

resilient skin

structured routine

skincare awareness
-
Resilience Against Inflammatory Skin Conditions: Despite the complexities of managing multiple skin concerns, your skin may exhibit a natural resilience against inflammatory conditions such as acne and rosacea, due to its dry nature and the careful attention required to manage its sensitivity and allergen exposure.
-
Structured Skincare Routine: Having a complex skin type means you're likely already in tune with your skin's needs and have a structured skincare routine in place. This disciplined approach is beneficial for addressing each concern systematically, allowing for better management of your skin's overall health.
-
Heightened Awareness of Ingredients: Being allergy-prone makes you more vigilant about the ingredients in your skincare products. This heightened awareness can lead to more informed choices, reducing the risk of adverse reactions and promoting skin health.

Pigmentation

Aging skin

Dehydration

Allergy Prone
-
Compromised Skin Barrier: The combination of aging, dehydration, pigmentation, and allergy-proneness implies that the skin barrier may be compromised, making it less effective at retaining moisture and protecting against external aggressors. This can lead to increased sensitivity and challenges in managing overall skin health.
-
Hyperpigmentation: ADPA skin has to contend with pigmentation issues. This could include uneven skin tone, dark spots, or melasma, which can be challenging to manage in conjunction with dryness and sensitivity.
-
Skin Aging: The natural aging process can be more pronounced in ADA Skin Types due to the dry nature of the skin and the potential for allergic reactions that may further stress the skin. Aging in this context is characterized by developing fine lines, wrinkles, and a loss of elasticity and firmness.
-
Dehydration and Dryness: Your ADPA skin type struggles with maintaining moisture due to an impaired barrier function, leading to dryness and flakiness. This can exacerbate the appearance of aging signs and make the skin more susceptible to irritants.
-
Allergy prone: Being prone to allergies means your skin may react more sensitively to various external factors, including certain skincare ingredients, environmental allergens, or dietary triggers. This can lead to redness, itching, and irritation, making it crucial to identify and avoid known allergens in your skincare and lifestyle.
include
- Anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial and pigmentation-disruptive ingredients.
- Broad spectrum sunscreen with antioxidants - preventing premature aging and protecting DNA.
- Effective barrier repair agents restore your skin's natural barrier and prevent premature aging.
- Hypoallergenic and pigmentation-disruptive ingredients.
- Skin-identical medical-grade ingredients that penetrate the skin to activate a biological response.
avoid
- Damaging lifestyle habits, e.g., smoking, tanning beds, excessive sun, and sugar consumption.
- Toners and foaming cleansers containing soap & sulfates.
- Fragrance in skincare products.
- Harsh anti-bacterial products that disrupt the skin's natural microbiome.
- Irritating plant extracts and essential oils that will trigger adverse reactions.
Aging . Dry . Pigmentation . Allergy during pregnancy
Treatment Objectives

Inhibit hyperpigmentation
Inhibit the pathways in the hyperpigmentation process to stop the stimulation, production and transfer of melanin (pigment cells).

Intensive Moisturization
Prioritize deep hydration to improve the skin's intrinsic ability to retain water and encourage the skin's production of natural moisturizing factors (NMFs) to sustain long-term hydration levels.

Skin Barrier Restoration
Repair and strengthen the skin's barrier function and enhance the production of natural barrier components like elastin and collagen to fortify the skin against allergens and environmental stressors.

Enhance Skin Texture
Employ mild resurfacing techniques that encourage collagen remodeling, improving skin resilience and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.

Prevent & Repair Skin Aging
Address premature aging with ingredients that support skin renewal and repair DNA damage. Antioxidants can protect against oxidative stress, while peptides and retinoids can stimulate collagen production.

Allergy Management
Implement a skincare regimen that minimizes the risk of allergic reactions with hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and non-irritating formulations.
Aging . Dry . Pigmentation . Allergy during pregnancy
beneficial active ingredients
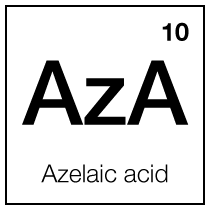
Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid, a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid, is an effective ingredient in dermatological treatments, particularly for acne, rosacea, and hyperpigmentation, with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Physiological Effects
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Azelaic acid reduces inflammation, effectively treating inflammatory skin conditions like acne and rosacea.
- Antimicrobial Action: It possesses antimicrobial properties that target acne-causing bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), helping to reduce acne outbreaks.
- Keratolytic Effects: It helps unclog pores and reduce the formation of comedones (black and whiteheads) by normalizing the shedding of skin cells.
- Depigmenting Agent: Azelaic acid effectively treats hyperpigmentation disorders, including melasma, as it inhibits tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne: Azelaic acid inhibits the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria on the skin’s surface, thereby reducing bacterial growth and inflammation. Its antibacterial activity is primarily against Propionibacterium acnes, a key bacterium involved in the development of acne. Furthermore, azelaic acid helps unclog pores and reduce skin cell buildup, effectively treating mild to moderate acne.
- Rosacea: Azelaic acid's anti-inflammatory action helps to reduce redness and swelling associated with rosacea. In addition, azelaic acid's ability to reduce keratinization (the process by which skin cells become more fibrous and less flexible) contributes to its effectiveness in this condition.
- Pigmentation: Azelaic acid effectively treats melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme in melanin production. This helps to reduce the formation of excess pigment and can lead to a more even skin tone.
References
- Fitton, A., & Goa, K. L. (1991). Azelaic Acid. Drugs.
- Gollnick, H., & Schramm, M. (1998). Topical drug treatment in acne. Dermatology.
- Passeron, T., et al. (2019). Melasma treatment: A novel approach using a topical agent that contains an anti-estrogen and a low-dose retinoid. G Ital Dermatol Venereol.
- Wolf, J. E., Kerrouche, N., & Arsonnaud, S. (2006). Efficacy and safety of once-daily metronidazole 1% gel compared with twice-daily azelaic acid 15% gel in the treatment of rosacea. Cutis, 77(4 Suppl), 3-11.
- Hollinger, J. C., Angra, K., & Halder, R. M. (2018). Are natural ingredients effective in the management of hyperpigmentation? A systematic review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology, 11(2), 28.
Alpha Arbutin
Alpha Arbutin is a derivative of hydroquinone and a biosynthetic active ingredient. Its primary action is inhibiting tyrosinase, a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Alpha Arbutin effectively reduces melanin production in the skin by inhibiting tyrosin activity. This gradually lightens hyperpigmented areas, such as age spots, melasma, and scars, resulting in a more even skin tone.
One of the significant advantages of Alpha Arbutin over other skin-lightening agents is its safety profile. Unlike hydroquinone, which has been associated with potential side effects and is restricted in many countries, Alpha Arbutin is considered safe and less irritating to the skin, even at higher concentrations. This makes it a suitable ingredient for all skin types, including sensitive skin.
In addition to its skin-lightening properties, Alpha Arbutin has also shown antioxidant effects, helping to protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
Physiological Effects
- Melanin Inhibition: Alpha Arbutin works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production in the skin. This action reduces the formation of melanin, leading to a lightening of skin pigmentation.
- Even Skin Tone: Regular use of alpha arbutin can lead to a more even skin tone overall, reducing the appearance of age spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Reduced Skin Discoloration: It effectively reduces the appearance of dark spots and areas of hyperpigmentation, such as those caused by acne, sun damage, or hormonal changes.
- Safer Alternative to Hydroquinone: While structurally similar to hydroquinone, alpha arbutin is a safer option with a lower risk of side effects.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Hyperpigmentation: Alpha arbutin treats melasma, sun spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne.
- Skin Brightening: Provide a more radiant and uniform skin tone.
- Anti-Aging: Reduce the appearance of age-related spots and uneven skin tone.
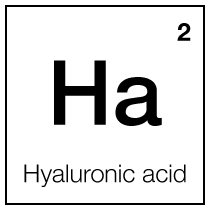
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found throughout the body's connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. Most abundantly present in the skin, eyes, and synovial fluid, HA is renowned for its exceptional capacity to retain moisture — a single gram can hold up to six liters of water.
In skincare, the primary appeal of hyaluronic acid lies in its unparalleled hydrating abilities. As a humectant, HA attracts and retains moisture from the environment, providing intense hydration to the skin. This hydrating property contributes significantly to maintaining skin plumpness, suppleness, and elasticity.
Beyond hydration, hyaluronic acid also plays a vital role in skin repair and regeneration. It supports the skin's healing and repair processes, and its anti-inflammatory properties help calm irritated skin. Moreover, HA's ability to promote collagen production, a crucial protein for skin elasticity, further underscores its anti-aging benefits.
The molecular size of hyaluronic acid influences its skin penetration and efficacy. High-molecular-weight HA remains on the skin's surface, providing hydration and forming a barrier against moisture loss. In contrast, low-molecular-weight HA penetrates deeper into the skin's layers, offering more profound hydrating and rejuvenating effects.
Hyaluronic acid's remarkable ability to hydrate, improve skin elasticity, aid in wound healing, and provide antioxidant protection makes it valuable in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly aging, dryness, and sensitive skin.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, significantly enhancing skin hydration and leading to plumper, more hydrated skin.
- Skin Elasticity and Wrinkle Reduction: By increasing skin moisture, it improves skin elasticity, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and gives the skin a more youthful appearance.
- Wound Healing: It plays a role in wound healing due to its ability to regulate inflammation levels and signal the body to build more blood vessels in the damaged area.
- Barrier Enhancement: Hyaluronic acid helps reinforce the skin's natural barriers, protecting against environmental factors and retaining moisture.
- Antioxidant Properties: It provides antioxidant defense against free-radical damage from the sun and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its ability to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity makes it popular in anti-aging skincare products.
- Dry Skin: Hyaluronic acid is beneficial in treating dry skin conditions by providing intense hydration.
- Wound Care: Its role in wound healing is leveraged in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments, and in healing minor cuts and abrasions.
- Acne Scars: It can help treat acne scars by promoting skin regeneration and reducing inflammation.
- Sensitive Skin: Hyaluronic acid is suitable for sensitive skin due to its gentle nature. It provides hydration without irritating.
References
- Papakonstantinou, E., Roth, M., & Karakiulakis, G. (2012). Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Jegasothy, S. M., Zabolotniaia, V., & Bielfeldt, S. (2014). Efficacy of a new topical nano-hyaluronic acid in humans. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Wollina, U., & Abdel-Naser, M. B. (2019). Hyaluronic acid in the treatment and prevention of skin diseases: Molecular biological, pharmaceutical and clinical aspects. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Zinc Pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione, a compound with potent antifungal and antibacterial properties, has established itself as a cornerstone in the treatment of various skin conditions, particularly those involving Malassezia yeast. Its effectiveness against seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, which are often associated with an overgrowth of Malassezia species, makes it a key ingredient for many dermatological conditions.
Zinc pyrithione’s mode of action is multifaceted, primarily targeting the membrane of fungi and bacteria, thereby disrupting their growth and replication. One of its significant mechanisms involves inhibiting fungal cell membrane transport by blocking the energy production pathway, which is crucial for cell survival.
In Malassezia, yeast, a natural inhabitant of the skin flora, can overgrow and cause conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff; zinc pyrithione's antifungal action is particularly beneficial. It reduces the yeast population on the skin, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with its overgrowth, such as flaking, irritation, and redness.
Its efficacy in treating seborrheic dermatitis is attributed to its ability to reduce the Malassezia count, diminish inflammatory responses, and soothe the skin. Similarly, in dandruff, which is often linked to an excess of Malassezia, zinc pyrithione effectively reduces flaking and itchiness, promoting a healthier scalp environment.
The efficacy of zinc pyrithione in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff is well-documented. Its safety profile and efficacy have been confirmed by numerous studies, with significant improvements observed in both scalp and skin conditions following regular use.
Physiological Effects
- Antifungal Activity: It is effective against a range of fungi, including those that cause dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Zinc Pyrithione inhibits the division of fungal cells, reducing their proliferation.
- Antibacterial Properties: This compound also exhibits antibacterial activity, making it useful in treating and preventing bacterial skin infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc Pyrithione can reduce inflammation, which is beneficial in alleviating symptoms of various inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps in regulating sebum production, which can be beneficial for oily skin and conditions like acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Zinc Pyrithione is a common ingredient in anti-dandruff shampoos and is effective in controlling the flaking and itching associated with these conditions.
- Psoriasis: It can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis, particularly in reducing scaling and redness.
- Acne: Due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc Pyrithione can be beneficial in the treatment of acne.
- Fungal Infections: It is effective in treating various fungal skin infections due to its antifungal properties.
References
- Warshaw, E. M., et al. (2005). Efficacy of Zinc Pyrithione in Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff. Dermatology.
- Pierard-Franchimont, C., et al. (2002). Antidandruff shampoo efficacy in dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Scheman, A., et al. (2000). Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Pyrithione. American Journal of Infection Control.
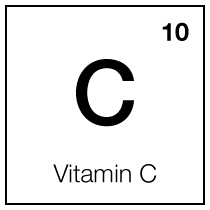
Vitamin C
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps to neutralize free radicals in the skin. These free radicals are generated by environmental stressors like UV radiation and pollution, which contribute to premature aging. By neutralizing these harmful molecules, vitamin C helps to prevent oxidative damage to the skin, thereby reducing signs of aging such as fine lines and wrinkles.
Another significant benefit of vitamin C is its role in collagen production. Collagen is a key protein that gives the skin its structure and firmness. As an essential cofactor for collagen biosynthesis, vitamin C helps to maintain skin elasticity and can aid in wound healing and the reduction of scars.
Vitamin C is also known for its skin-brightening properties. It helps to inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. By reducing melanin formation, vitamin C can help to lighten hyperpigmentation and even out skin tone, leading to a brighter and more radiant complexion.
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is a stable, oil-soluble form of vitamin C. Unlike ascorbic acid, which is water-soluble and can be unstable in certain formulations, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is more stable and can penetrate the skin more effectively due to its lipid-soluble nature. This allows it to reach the deeper layers of the skin where it can stimulate collagen production and provide antioxidant protection.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Properties: Powerful antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals caused by UV radiation and pollution, preventing oxidative stress and damage to the skin.
- Collagen Synthesis: It plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, aiding in maintaining skin firmness and elasticity, and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Brightening: Effective in reducing hyperpigmentation and evening out skin tone by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is responsible for melanin production.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it provides photoprotection by neutralizing free radicals induced by UV exposure.
THD Specific benefits
- Stable form of Vitamin C: Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate is a more stable, lipid-soluble form of vitamin C, allowing for better skin penetration and less irritation compared to other forms.
- Enhanced Collagen Production: It has been shown to stimulate collagen production more effectively than ascorbic acid, aiding in anti-aging and skin rejuvenation.
- Hydration and Barrier Function: Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it helps in enhancing skin hydration and reinforcing the skin barrier.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Reduce signs of aging and improve skin texture.
- Hyperpigmentation: Effective in treating hyperpigmentation, sun spots, and melasma.
- Sun Damage: Help in mitigating the effects of sun damage and providing some level of photoprotection.
- General Skin Health: Both forms can improve overall skin health by boosting collagen production and providing antioxidant protection.
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate specific benefits
- Stable form of Vitamin C: Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate is a more stable, lipid-soluble form of vitamin C, allowing for better skin penetration and less irritation compared to other forms.
- Enhanced Collagen Production: It has been shown to stimulate collagen production more effectively than ascorbic acid, aiding in anti-aging and skin rejuvenation.
- Hydration and Barrier Function: Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it helps in enhancing skin hydration and reinforcing the skin barrier.
References
- Pullar, J. M., et al. (2017). The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients.
- Murray, J. C., et al. (2008). A Topical Antioxidant Solution Containing Vitamins C and E Stabilized by Ferulic Acid Provides Protection for Human Skin Against Damage Caused by Ultraviolet Irradiation. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Al-Niaimi, F., & Chiang, N. Y. Z. (2017). Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
Ceramides
Ceramides, a family of lipid molecules naturally present in the skin, are integral to the structure and function of the skin barrier. They are a type of lipid that, along with cholesterol and fatty acids, forms a critical part of the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin. This layer is essential for maintaining skin hydration and protecting against environmental aggressors.
Ceramides, which make up about 50% of the skin's lipid composition, play a pivotal role in maintaining the skin's barrier integrity and preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL). By doing so, they help keep the skin hydrated and supple.
The loss or reduction of ceramides in the skin barrier is associated with several dermatological conditions, including eczema and psoriasis, where the skin becomes dry, itchy, and prone to irritation and infection. Studies have shown that the application of ceramide-containing moisturizers can effectively improve skin barrier function and increase skin hydration levels.
Ceramides are particularly beneficial for aging skin, which naturally loses ceramides over time, leading to drier and more fragile skin. By replenishing the skin's ceramide content, these products can help combat the signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles.
Ceramides are integral to maintaining skin health, particularly in conditions where the skin barrier is compromised. Their role in hydrating the skin, reducing sensitivity, and improving barrier function makes them an essential component in the management of various dermatological conditions, especially eczema, psoriasis, and dry or aging skin.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function: Ceramides are critical components of the skin's lipid barrier. They help to prevent moisture loss and protect against environmental aggressors like pollutants and irritants.
- Hydration: By maintaining the barrier integrity, ceramides keep the skin hydrated, preventing dryness and keeping the skin supple.
- Reducing Skin Sensitivity: They play a role in reducing skin sensitivity and irritation, helping to calm inflamed and reactive skin.
- Anti-aging Properties: Ceramides can improve skin elasticity and firmness, helping to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Wound Healing: There is evidence to suggest that ceramides can aid in the skin's natural wound healing process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis: Ceramides are often used in the treatment of eczema and atopic dermatitis, where the skin barrier is compromised, leading to dryness, itching, and inflammation.
- Psoriasis: They can help in managing psoriasis by maintaining skin hydration and barrier function, reducing scaling and dryness.
- Aging Skin: Ceramide-containing products are beneficial in anti-aging regimens due to their ability to improve skin barrier function and elasticity.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): In the treatment of dry skin, ceramides help in restoring skin hydration and barrier function.
- Sensitive Skin: Products containing ceramides are suitable for sensitive skin as they help to restore the skin's natural barrier and reduce irritation.
References
- Del Rosso, J. Q., & Levin, J. (2011). The clinical relevance of maintaining the functional integrity of the stratum corneum in both healthy and disease-affected skin. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Farwanah, H., Wohlrab, J., Neubert, R. H. H., & Raith, K. (2005). Ceramides and skin function. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Di Nardo, A., Wertz, P., Giannetti, A., & Seidenari, S. (1998). Ceramide and cholesterol composition of the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica.
Bakuchiol
Bakuchiol's mechanism of action is similar to retinol's; it stimulates collagen production and accelerates cell turnover, improving skin texture and tone. It also helps reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation, making it an effective ingredient in anti-aging skincare products.
One of the key advantages of bakuchiol over traditional retinol is its gentleness on the skin. Retinol is known for potential side effects like dryness, redness, and irritation, particularly in sensitive skin or when used in high concentrations. Bakuchiol, however, is far less irritating. In addition to its anti-aging properties, bakuchiol exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, further contributing to its skin benefits. It helps protect the skin from oxidative stress and can soothe it, reducing redness and inflammation.
Bakuchiol's retinol-like effects and its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties make it an effective ingredient for various skin concerns, especially for those seeking natural alternatives in anti-aging and acne treatment.
Physiological Effects
- Retinol-like Function: Bakuchiol mimics the actions of retinol, stimulating collagen production. This helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improves skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Properties: It offers antioxidant benefits, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Bakuchiol has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help soothe the skin and reduce redness and irritation.
- Improved Skin Tone and Texture: Regular use of bakuchiol can improve skin tone and texture, making it smoother and more even.
- Acne Management: Bakuchiol's antibacterial properties and ability to regulate sebum production make it effective in managing acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Bakuchiol is popular in anti-aging skincare because it stimulates collagen production and reduces signs of aging.
- Sensitive Skin: As a gentler alternative to retinol, it is suitable for sensitive skin types that cannot tolerate traditional retinoids.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties are beneficial in acne treatments.
- Hyperpigmentation: Bakuchiol can help treat hyperpigmentation, enhance skin radiance, and reduce dark spots.
References
- Chaudhuri, R. K., & Bojanowski, K. (2014). Bakuchiol: a retinol-like functional compound revealed by gene expression profiling and clinically proven to have anti-aging effects. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Dhaliwal, S., et al. (2019). Prospective, randomized, double-blind assessment of topical bakuchiol and retinol for facial photoageing. British Journal of Dermatology.
- Sivamani, R. K., et al. (2019). Clinical efficacy of a bakuchiol, niacinamide and zinc pyrithione formulation in facial sebum control and mild acne. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is a fundamental aspect of skin care and preventive dermatology. It's essential for reducing the risk of skin cancers and photoaging and maintaining overall skin health in the face of constant exposure to UV radiation.
Sunscreen is a vital skincare product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Two primary types of UV radiation affect the skin: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging and long-term skin damage, whereas UVB rays cause sunburn and play a key role in developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen products work by either absorbing, reflecting, or scattering sunlight. They contain chemical compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into a small amount of heat or physical compounds (like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) that act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV light away from the skin.
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF). SPF indicates how well the sunscreen protects against UVB rays. For example, an SPF of 30 means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn than without sunscreen. However, it's important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% UV rays.
Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can reduce the risk of skin cancer, prevent sunburn, and slow down the skin's aging process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Prevention of Sunburn: Sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. This reduces the immediate risk of skin damage and discomfort.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Regular use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, especially melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
- Prevention of Photoaging: Sunscreen also shields the skin from UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for photoaging, including wrinkles, leathery skin, and sunspots.
- Protection Against Photosensitivity: Sunscreen helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure for individuals with photosensitive skin conditions like lupus or rosacea.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: It aids in preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma, conditions exacerbated by sun exposure.
- General Skin Health: Sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health and integrity by protecting the skin from UV damage.
References
- Burnett, M. E., & Wang, S. Q. (2011). Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.
- Green, A. C., et al. (2011). Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine.
Aging . Dry . Pigmentation . Allergy during pregnancy
products in your treatment pack








Itch Relief

Anti-Acne

↓ inflammation

anti-redness

Anti-microbial
A powerful hypoallergenic medicated solution with beneficial properties attributed to its active constituent, Zinc Pyrithione. This chemical compound, FDA-approved and clinically recognized, delivers strong antibacterial and antifungal action, making the cleanser an ideal choice for managing skin conditions associated with redness, flaking, irritation, and itching.
Zinc Pyrithione's efficacy, compounded by a gentle cleansing base, facilitates the lifting and removing of impurities, leaving the complexion refreshed. Concurrently, it sustains a tranquil skin environment, reducing inflammation and discomfort. As a daily cleansing aid, Medi-Zinc Cleanser proposes a reliable, scientifically-backed intervention in fostering skin health and comfort.
Zinc Pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione, a compound with potent antifungal and antibacterial properties, has established itself as a cornerstone in the treatment of various skin conditions, particularly those involving Malassezia yeast. Its effectiveness against seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, which are often associated with an overgrowth of Malassezia species, makes it a key ingredient for many dermatological conditions.
Zinc pyrithione’s mode of action is multifaceted, primarily targeting the membrane of fungi and bacteria, thereby disrupting their growth and replication. One of its significant mechanisms involves inhibiting fungal cell membrane transport by blocking the energy production pathway, which is crucial for cell survival.
In Malassezia, yeast, a natural inhabitant of the skin flora, can overgrow and cause conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff; zinc pyrithione's antifungal action is particularly beneficial. It reduces the yeast population on the skin, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with its overgrowth, such as flaking, irritation, and redness.
Its efficacy in treating seborrheic dermatitis is attributed to its ability to reduce the Malassezia count, diminish inflammatory responses, and soothe the skin. Similarly, in dandruff, which is often linked to an excess of Malassezia, zinc pyrithione effectively reduces flaking and itchiness, promoting a healthier scalp environment.
The efficacy of zinc pyrithione in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff is well-documented. Its safety profile and efficacy have been confirmed by numerous studies, with significant improvements observed in both scalp and skin conditions following regular use.
Physiological Effects
- Antifungal Activity: It is effective against a range of fungi, including those that cause dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Zinc Pyrithione inhibits the division of fungal cells, reducing their proliferation.
- Antibacterial Properties: This compound also exhibits antibacterial activity, making it useful in treating and preventing bacterial skin infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc Pyrithione can reduce inflammation, which is beneficial in alleviating symptoms of various inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps in regulating sebum production, which can be beneficial for oily skin and conditions like acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Zinc Pyrithione is a common ingredient in anti-dandruff shampoos and is effective in controlling the flaking and itching associated with these conditions.
- Psoriasis: It can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis, particularly in reducing scaling and redness.
- Acne: Due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc Pyrithione can be beneficial in the treatment of acne.
- Fungal Infections: It is effective in treating various fungal skin infections due to its antifungal properties.
References
- Warshaw, E. M., et al. (2005). Efficacy of Zinc Pyrithione in Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff. Dermatology.
- Pierard-Franchimont, C., et al. (2002). Antidandruff shampoo efficacy in dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Scheman, A., et al. (2000). Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Pyrithione. American Journal of Infection Control.






SIZE: 30 mL

Antioxidant

Even Skin Tone

↑ Collagen

anti-aging

Moisturizing
A potent antioxidant formulation enriched with Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate, a highly stable and powerful form of Vitamin C. This serum is designed to brighten the skin tone and combat signs of aging effectively. Its unique blend of ingredients, including Vitamin F essential fatty acids, Niacinamide, and low molecular weight Hyaluronic Acid, provides multi-depth serum penetration and optimal hydration.
With its remarkable ability to stimulate collagen production, this hyper-strength treatment serum promotes skin elasticity and reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Additionally, it inhibits melanin production, leading to a brighter complexion while counteracting the effects of UV exposure and environmental damage.
Collagen Serum's expert formulation works synergistically to plump the skin, enhance skin tone, and refine pore size, resulting in a visibly smoother and more youthful appearance. Its rich antioxidant properties contribute to repairing and rejuvenating the skin, promoting a healthier complexion overall.
Vitamin C
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize skin free radicals. These free radicals are generated by environmental stressors like UV radiation and pollution, which contribute to premature aging. By neutralizing these harmful molecules, vitamin C helps prevent oxidative skin damage, thereby reducing signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles.
Another significant benefit of vitamin C is its role in collagen production. Collagen is a key protein that gives the skin its structure and firmness. As an essential cofactor for collagen biosynthesis, vitamin C helps maintain skin elasticity and can aid in wound healing and scar reduction.
Vitamin C is also known for its skin-brightening properties. It helps to inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. By reducing melanin formation, vitamin C can help lighten hyperpigmentation and even skin tone, leading to a brighter and more radiant complexion.
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is a stable, oil-soluble form of vitamin C. Unlike ascorbic acid, which is water-soluble and can be unstable in certain formulations, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is more stable. Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it can penetrate the skin more effectively, reaching the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating collagen production, and providing antioxidant protection.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Properties: Powerful antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals caused by UV radiation and pollution, preventing oxidative stress and damage to the skin.
- Collagen Synthesis: It plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, aiding in maintaining skin firmness and elasticity and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Brightening: Effective in reducing hyperpigmentation and evening out skin tone by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is responsible for melanin production.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it provides photoprotection by neutralizing free radicals induced by UV exposure.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Reduce signs of aging and improve skin texture.
- Hyperpigmentation: Effective in treating hyperpigmentation, sun spots, and melasma.
- Sun Damage: Help mitigate the effects of sun damage and provide some level of photoprotection.
- General Skin Health: Both forms can improve overall skin health by boosting collagen production and providing antioxidant protection.
THD Specific benefits
- Stable form of Vitamin C: Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate is a more stable, lipid-soluble vitamin C, allowing for better skin penetration and less irritation than other forms.
- Enhanced Collagen Production: It has been shown to stimulate collagen production more effectively than ascorbic acid, aiding in anti-aging and skin rejuvenation.
- Hydration and Barrier Function: Due to its lipid-soluble nature, it enhances skin hydration and reinforces the skin barrier.
References
- Pullar, J. M., et al. (2017). The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients.
- Murray, J. C., et al. (2008). A Topical Antioxidant Solution Containing Vitamins C and E Stabilized by Ferulic Acid Provides Protection for Human Skin Against Damage Caused by Ultraviolet Irradiation. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Al-Niaimi, F., & Chiang, N. Y. Z. (2017). Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found throughout the body's connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. Most abundantly present in the skin, eyes, and synovial fluid, HA is renowned for its exceptional capacity to retain moisture — a single gram can hold up to six liters of water.
In skincare, the primary appeal of hyaluronic acid lies in its unparalleled hydrating abilities. As a humectant, HA attracts and retains moisture from the environment, providing intense hydration to the skin. This hydrating property contributes significantly to maintaining skin plumpness, suppleness, and elasticity.
Beyond hydration, hyaluronic acid also plays a vital role in skin repair and regeneration. It supports the skin's healing and repair processes, and its anti-inflammatory properties help calm irritated skin. Moreover, HA's ability to promote collagen production, a crucial protein for skin elasticity, further underscores its anti-aging benefits.
The molecular size of hyaluronic acid influences its skin penetration and efficacy. High-molecular-weight HA remains on the skin's surface, providing hydration and forming a barrier against moisture loss. In contrast, low-molecular-weight HA penetrates deeper into the skin's layers, offering more profound hydrating and rejuvenating effects.
Hyaluronic acid's remarkable ability to hydrate, improve skin elasticity, aid in wound healing, and provide antioxidant protection makes it valuable in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly aging, dryness, and sensitive skin.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, significantly enhancing skin hydration and leading to plumper, more hydrated skin.
- Skin Elasticity and Wrinkle Reduction: By increasing skin moisture, it improves skin elasticity, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and gives the skin a more youthful appearance.
- Wound Healing: It plays a role in wound healing due to its ability to regulate inflammation levels and signal the body to build more blood vessels in the damaged area.
- Barrier Enhancement: Hyaluronic acid helps reinforce the skin's natural barriers, protecting against environmental factors and retaining moisture.
- Antioxidant Properties: It provides antioxidant defense against free-radical damage from the sun and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its ability to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity makes it popular in anti-aging skincare products.
- Dry Skin: Hyaluronic acid is beneficial in treating dry skin conditions by providing intense hydration.
- Wound Care: Its role in wound healing is leveraged in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments, and in healing minor cuts and abrasions.
- Acne Scars: It can help treat acne scars by promoting skin regeneration and reducing inflammation.
- Sensitive Skin: Hyaluronic acid is suitable for sensitive skin due to its gentle nature. It provides hydration without irritating.
References
- Papakonstantinou, E., Roth, M., & Karakiulakis, G. (2012). Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Jegasothy, S. M., Zabolotniaia, V., & Bielfeldt, S. (2014). Efficacy of a new topical nano-hyaluronic acid in humans. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Wollina, U., & Abdel-Naser, M. B. (2019). Hyaluronic acid in the treatment and prevention of skin diseases: Molecular biological, pharmaceutical and clinical aspects. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Hydrotensyl Complex
An active ingredient made from the combination of 3 powerful actives with extraordinary benefits for the skin:
- Honey Extract
- Marine native Collagen
- Marine Hydrolyzed Elastin
Honey Extract
- Provides natural moisturising factor analogue substances to skin cells.
- It also provides the skin with components with a vital capacity for hydro-retention and hydro-regulation.
- Mechanisms of action on skin cells include antioxidant activity and the induction of cytokines, and matrix metalloproteinase expression.
Marine native Collagen
Native Collagen has a high molecular weight, that leaves a protective film on the skin with tensor effects and remarkable moisturizing capabilities.
Marine Hydrolyzed Elastin
- Provide nutrients and amino acids that the fibroblasts (type of skin cell) will use to produce new fibres of elastin and collagen.
- It contains the peptides and amino acids of elastin: Aspartic Acid, Theorine, Serine, Glutamic Acid, Proline, Glycine, Lysine, and Arginine.
It is a complete active ingredient from which the skin will get substances to nourish, increase its moisture, get external protection against damaging substances, and decrease its wrinkles.






SIZE: 30 mL

Even Skin Tone

Moisturizing

anti-redness

anti-aging

↓ inflammation
A scientifically formulated correction serum that targets various skin concerns, promoting a healthy and radiant complexion. Its powerful blend of multi-tasking active ingredients is supported by peer-reviewed medical literature, ensuring its effectiveness in improving and preventing hyperpigmentation, melasma, redness, acne, rosacea, premature aging, and pigmentation.
The key active ingredients in Litaderm Serum work synergistically to deliver remarkable benefits. Niacinamide, at 10% concentration, enhances skin appearance by reducing hyperpigmentation, promoting even skin tone, and combating inflammation related to acne and rosacea. At 1%, Bakuchiol provides targeted treatment for signs of aging and skin damage, supporting a youthful complexion. With a potent 10% concentration, Azelaic acid reduces hyperpigmentation, redness, and inflammation, contributing to overall healthier skin. Arbutin, comprising 4% of the formula, further aids in correcting hyperpigmentation and promoting a more even complexion.
With its carefully selected ingredients, Litaderm Serum offers a dynamic formulation that comprehensively addresses various skin concerns. Supported by scientific evidence, this serum effectively targets hyperpigmentation, melasma, redness, acne, rosacea, premature aging, and pigmentation. Regularly using Litaderm Serum improves skin tone, texture, and overall radiance, resulting in healthy, radiant, and even-toned skin. Experience the benefits of this targeted approach to achieve a revitalized and rejuvenated appearance.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid, a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid, is an effective ingredient in dermatological treatments, particularly for acne, rosacea, and hyperpigmentation, with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Physiological Effects
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Azelaic acid reduces inflammation, effectively treating inflammatory skin conditions like acne and rosacea.
- Antimicrobial Action: It possesses antimicrobial properties that target acne-causing bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), helping to reduce acne outbreaks.
- Keratolytic Effects: It helps unclog pores and reduce the formation of comedones (black and whiteheads) by normalizing the shedding of skin cells.
- Depigmenting Agent: Azelaic acid effectively treats hyperpigmentation disorders, including melasma, as it inhibits tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne: Azelaic acid inhibits the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria on the skin’s surface, thereby reducing bacterial growth and inflammation. Its antibacterial activity is primarily against Propionibacterium acnes, a key bacterium involved in the development of acne. Furthermore, azelaic acid helps unclog pores and reduce skin cell buildup, effectively treating mild to moderate acne.
- Rosacea: Azelaic acid's anti-inflammatory action helps to reduce redness and swelling associated with rosacea. In addition, azelaic acid's ability to reduce keratinization (the process by which skin cells become more fibrous and less flexible) contributes to its effectiveness in this condition.
- Pigmentation: Azelaic acid effectively treats melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme in melanin production. This helps to reduce the formation of excess pigment and can lead to a more even skin tone.
References
- Fitton, A., & Goa, K. L. (1991). Azelaic Acid. Drugs.
- Gollnick, H., & Schramm, M. (1998). Topical drug treatment in acne. Dermatology.
- Passeron, T., et al. (2019). Melasma treatment: A novel approach using a topical agent that contains an anti-estrogen and a low-dose retinoid. G Ital Dermatol Venereol.
- Wolf, J. E., Kerrouche, N., & Arsonnaud, S. (2006). Efficacy and safety of once-daily metronidazole 1% gel compared with twice-daily azelaic acid 15% gel in the treatment of rosacea. Cutis, 77(4 Suppl), 3-11.
- Hollinger, J. C., Angra, K., & Halder, R. M. (2018). Are natural ingredients effective in the management of hyperpigmentation? A systematic review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology, 11(2), 28.
Alpha Arbutin
Alpha Arbutin is a derivative of hydroquinone and a biosynthetic active ingredient. Its primary action is inhibiting tyrosinase, a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Alpha Arbutin effectively reduces melanin production in the skin by inhibiting tyrosin activity. This gradually lightens hyperpigmented areas, such as age spots, melasma, and scars, resulting in a more even skin tone.
One of the significant advantages of Alpha Arbutin over other skin-lightening agents is its safety profile. Unlike hydroquinone, which has been associated with potential side effects and is restricted in many countries, Alpha Arbutin is considered safe and less irritating to the skin, even at higher concentrations. This makes it a suitable ingredient for all skin types, including sensitive skin.
In addition to its skin-lightening properties, Alpha Arbutin has also shown antioxidant effects, helping to protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
Physiological Effects
- Melanin Inhibition: Alpha Arbutin works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production in the skin. This action reduces the formation of melanin, leading to a lightening of skin pigmentation.
- Even Skin Tone: Regular use of alpha arbutin can lead to a more even skin tone overall, reducing the appearance of age spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Reduced Skin Discoloration: It effectively reduces the appearance of dark spots and areas of hyperpigmentation, such as those caused by acne, sun damage, or hormonal changes.
- Safer Alternative to Hydroquinone: While structurally similar to hydroquinone, alpha arbutin is a safer option with a lower risk of side effects.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Hyperpigmentation: Alpha arbutin treats melasma, sun spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne.
- Skin Brightening: Provide a more radiant and uniform skin tone.
- Anti-Aging: Reduce the appearance of age-related spots and uneven skin tone.
Bakuchiol
Bakuchiol's mechanism of action is similar to retinol's; it stimulates collagen production and accelerates cell turnover, improving skin texture and tone. It also helps reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation, making it an effective ingredient in anti-aging skincare products.
One of the key advantages of bakuchiol over traditional retinol is its gentleness on the skin. Retinol is known for potential side effects like dryness, redness, and irritation, particularly in sensitive skin or when used in high concentrations. Bakuchiol, however, is far less irritating. In addition to its anti-aging properties, bakuchiol exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, further contributing to its skin benefits. It helps protect the skin from oxidative stress and can soothe it, reducing redness and inflammation.
Bakuchiol's retinol-like effects and its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties make it an effective ingredient for various skin concerns, especially for those seeking natural alternatives in anti-aging and acne treatment.
Physiological Effects
- Retinol-like Function: Bakuchiol mimics the actions of retinol, stimulating collagen production. This helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improves skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Properties: It offers antioxidant benefits, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Bakuchiol has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help soothe the skin and reduce redness and irritation.
- Improved Skin Tone and Texture: Regular use of bakuchiol can improve skin tone and texture, making it smoother and more even.
- Acne Management: Bakuchiol's antibacterial properties and ability to regulate sebum production make it effective in managing acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Bakuchiol is popular in anti-aging skincare because it stimulates collagen production and reduces signs of aging.
- Sensitive Skin: As a gentler alternative to retinol, it is suitable for sensitive skin types that cannot tolerate traditional retinoids.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties are beneficial in acne treatments.
- Hyperpigmentation: Bakuchiol can help treat hyperpigmentation, enhance skin radiance, and reduce dark spots.
References
- Chaudhuri, R. K., & Bojanowski, K. (2014). Bakuchiol: a retinol-like functional compound revealed by gene expression profiling and clinically proven to have anti-aging effects. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Dhaliwal, S., et al. (2019). Prospective, randomized, double-blind assessment of topical bakuchiol and retinol for facial photoageing. British Journal of Dermatology.
- Sivamani, R. K., et al. (2019). Clinical efficacy of a bakuchiol, niacinamide and zinc pyrithione formulation in facial sebum control and mild acne. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.








irritated skin

aging

Dry skin

Inflammation

Allergies
A cutting-edge product formulated to restore the skin barrier function on a physiological level. With its Triple Physiological Lipid-based Technology, this ultra-advanced formula combines various moisturizing agents to create an intelligent moisturizing complex.
It contains patented intelligent hydration technology that operates through a dual mechanism to optimize skin moisturization. Firstly, it forms an intelligent structural layer on the skin's surface, providing immediate hydration and sealing in moisture. Secondly, it regulates water loss from within by reinforcing the skin's natural barrier, preventing excessive moisture evaporation.
Enriched™ is particularly effective for individuals with very dry skin conditions such as eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, and ichthyosis. By replenishing the skin's essential lipids and lamellar bilayers, this intensely moisturizing complex promotes optimal recovery for dry skin and aids in repairing impaired barrier function.
The results of using Enriched™ are remarkable. Your skin will experience a newfound smoothness with deep hydration that lasts. Moreover, your skin’s resilience will improve, allowing it to withstand external aggressors better and maintain optimal health.
Ceramides
Ceramides, a family of lipid molecules naturally present in the skin, are integral to the structure and function of the skin barrier. They are a type of lipid that, along with cholesterol and fatty acids, forms a critical part of the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin. This layer is essential for maintaining skin hydration and protecting against environmental aggressors.
Ceramides, which make up about 50% of the skin's lipid composition, play a pivotal role in maintaining the skin's barrier integrity and preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL). By doing so, they help keep the skin hydrated and supple.
The loss or reduction of ceramides in the skin barrier is associated with several dermatological conditions, including eczema and psoriasis, where the skin becomes dry, itchy, and prone to irritation and infection. Studies have shown that the application of ceramide-containing moisturizers can effectively improve skin barrier function and increase skin hydration levels.
Ceramides are particularly beneficial for aging skin, which naturally loses ceramides over time, leading to drier and more fragile skin. By replenishing the skin's ceramide content, these products can help combat the signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles.
Ceramides are integral to maintaining skin health, particularly in conditions where the skin barrier is compromised. Their role in hydrating the skin, reducing sensitivity, and improving barrier function makes them an essential component in the management of various dermatological conditions, especially eczema, psoriasis, and dry or aging skin.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function: Ceramides are critical components of the skin's lipid barrier. They help to prevent moisture loss and protect against environmental aggressors like pollutants and irritants.
- Hydration: By maintaining the barrier integrity, ceramides keep the skin hydrated, preventing dryness and keeping the skin supple.
- Reducing Skin Sensitivity: They play a role in reducing skin sensitivity and irritation, helping to calm inflamed and reactive skin.
- Anti-aging Properties: Ceramides can improve skin elasticity and firmness, helping to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Wound Healing: There is evidence to suggest that ceramides can aid in the skin's natural wound healing process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis: Ceramides are often used in the treatment of eczema and atopic dermatitis, where the skin barrier is compromised, leading to dryness, itching, and inflammation.
- Psoriasis: They can help in managing psoriasis by maintaining skin hydration and barrier function, reducing scaling and dryness.
- Aging Skin: Ceramide-containing products are beneficial in anti-aging regimens due to their ability to improve skin barrier function and elasticity.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): In the treatment of dry skin, ceramides help in restoring skin hydration and barrier function.
- Sensitive Skin: Products containing ceramides are suitable for sensitive skin as they help to restore the skin's natural barrier and reduce irritation.
References
- Del Rosso, J. Q., & Levin, J. (2011). The clinical relevance of maintaining the functional integrity of the stratum corneum in both healthy and disease-affected skin. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Farwanah, H., Wohlrab, J., Neubert, R. H. H., & Raith, K. (2005). Ceramides and skin function. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Di Nardo, A., Wertz, P., Giannetti, A., & Seidenari, S. (1998). Ceramide and cholesterol composition of the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
d-Panthenol
d-Panthenol's multifaceted effects on skin hydration, barrier strengthening, and wound healing make it a valuable component in the management of various dermatological conditions, from dry skin to post-procedure care.
d-Panthenol, also known as pro-vitamin B5, is a popular dermatological ingredient due to its beneficial effects on the skin. Here's a brief overview of its physiological effects and roles in managing various skin conditions:
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: d-Panthenol is a humectant, meaning it helps to attract and retain moisture in the skin. This leads to increased skin hydration, which can improve skin softness and elasticity.
- Wound Healing and Repair: It plays a role in the synthesis of lipids and proteins, essential for skin repair. d-Panthenol has been shown to accelerate re-epithelialization in wound healing.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effect: d-Panthenol can reduce inflammation, making it beneficial in treating skin irritations and erythema.
- Skin Barrier Strengthening: By enhancing the synthesis of lipids and proteins, d-Panthenol contributes to the strengthening of the skin's barrier function, protecting against irritants and environmental damage.
- Soothing and Softening: It soothes the skin and makes it feel softer and smoother, which can be particularly beneficial for dry or rough skin textures.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Minor Wounds and Skin Irritations: Due to its role in skin repair and anti-inflammatory properties, d-Panthenol is used in the treatment of minor wounds, cuts, and skin irritations.
- Dermatitis and Eczema: It helps in managing conditions like dermatitis and eczema by reducing inflammation and enhancing skin barrier function.
- Dry Skin Conditions (Xerosis): Its moisturizing properties make it effective in treating dry skin, providing relief from itching and scaling.
- Post-procedure Care: d-Panthenol is often used in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments or chemical peels, to aid in skin recovery and reduce inflammation.
References
- Proksch, E., & Nissen, H. P. (2002). Dexpanthenol enhances skin barrier repair and reduces inflammation after sodium lauryl sulphate-induced irritation. Journal of Dermatological Treatment.
- Ebner, F., Heller, A., Rippke, F., & Tausch, I. (2002). Topical use of dexpanthenol in skin disorders. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Camargo, F. B. Jr, Gaspar, L. R., & Maia Campos, P. M. B. G. (2011). Skin moisturizing effects of panthenol-based formulations. Journal of Cosmetic Science.
Essential Fatty Acids
Essential Fatty Acids: Nourishing Your Skin from Within
In the realm of dermatological science, essential fatty acids (EFAs) have emerged as unsung heroes, offering a multifaceted approach to improving skin health in patients with conditions such as eczema and dry skin.
Pharmacological Advantages
EFAs are not only instrumental in maintaining the skin's structural integrity but also possess anti-inflammatory properties. They serve as precursors for pro-resolving lipid mediators like resolvins and protectins, which help reduce skin inflammation, itching, and redness—common symptoms of eczema.
Physiological Harmony
EFAs contribute to maintaining the balance of skin hydration. They enhance the skin's ability to retain water, leaving it supple and hydrated. Moreover, EFAs can modulate the skin's immune response, reducing the severity of allergic reactions and flare-ups often seen in dermatological conditions like eczema.
Biochemical Brilliance
Essential fatty acids, including omega-3 and omega-6, are the building blocks of the skin's lipid barrier. This barrier acts as a protective shield, preventing excessive moisture loss and shielding the skin from external aggressors. EFAs play a pivotal role in maintaining this barrier's integrity by contributing to the synthesis of ceramides and lipids that bind skin cells together.
References
- Elias, P. M. et al. (2008). Skin diseases associated with decreased epidermal lipogenesis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1141(1), 1-13.
- Ziboh, V. A. et al. (2000). Biochemical basis of the essential fatty acid requirement for normative growth in neonatal baboons. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 71(1), 3-11.
- Serhan, C. N. (2014). Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature, 510(7503), 92-101.
- Levesque, A. et al. (2018). Omega-3 fatty acids: Anti-inflammatory and skin barrier benefits. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Keys to Nutritional Health, 303-315.
- Nicolaou, A. (2013). Eicosanoids in skin inflammation. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids, 88(1), 131-138.
- Meydani, S. N. et al. (2018). Nutrition interventions in aging and age-associated diseases. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1418(1), 34-51.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found throughout the body's connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. Most abundantly present in the skin, eyes, and synovial fluid, HA is renowned for its exceptional capacity to retain moisture — a single gram can hold up to six liters of water.
In skincare, the primary appeal of hyaluronic acid lies in its unparalleled hydrating abilities. As a humectant, HA attracts and retains moisture from the environment, providing intense hydration to the skin. This hydrating property contributes significantly to maintaining skin plumpness, suppleness, and elasticity.
Beyond hydration, hyaluronic acid also plays a vital role in skin repair and regeneration. It supports the skin's healing and repair processes, and its anti-inflammatory properties help calm irritated skin. Moreover, HA's ability to promote collagen production, a crucial protein for skin elasticity, further underscores its anti-aging benefits.
The molecular size of hyaluronic acid influences its skin penetration and efficacy. High-molecular-weight HA remains on the skin's surface, providing hydration and forming a barrier against moisture loss. In contrast, low-molecular-weight HA penetrates deeper into the skin's layers, offering more profound hydrating and rejuvenating effects.
Hyaluronic acid's remarkable ability to hydrate, improve skin elasticity, aid in wound healing, and provide antioxidant protection makes it valuable in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly aging, dryness, and sensitive skin.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, significantly enhancing skin hydration and leading to plumper, more hydrated skin.
- Skin Elasticity and Wrinkle Reduction: By increasing skin moisture, it improves skin elasticity, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and gives the skin a more youthful appearance.
- Wound Healing: It plays a role in wound healing due to its ability to regulate inflammation levels and signal the body to build more blood vessels in the damaged area.
- Barrier Enhancement: Hyaluronic acid helps reinforce the skin's natural barriers, protecting against environmental factors and retaining moisture.
- Antioxidant Properties: It provides antioxidant defense against free-radical damage from the sun and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its ability to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity makes it popular in anti-aging skincare products.
- Dry Skin: Hyaluronic acid is beneficial in treating dry skin conditions by providing intense hydration.
- Wound Care: Its role in wound healing is leveraged in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments, and in healing minor cuts and abrasions.
- Acne Scars: It can help treat acne scars by promoting skin regeneration and reducing inflammation.
- Sensitive Skin: Hyaluronic acid is suitable for sensitive skin due to its gentle nature. It provides hydration without irritating.
References
- Papakonstantinou, E., Roth, M., & Karakiulakis, G. (2012). Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Jegasothy, S. M., Zabolotniaia, V., & Bielfeldt, S. (2014). Efficacy of a new topical nano-hyaluronic acid in humans. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Wollina, U., & Abdel-Naser, M. B. (2019). Hyaluronic acid in the treatment and prevention of skin diseases: Molecular biological, pharmaceutical and clinical aspects. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.






SIZE: 50 mL

Antioxidant

anti-aging

DNA repair

sun protection

Moisturizing
A pioneering sunscreen offering superior protection against the sun while preserving your skin's cellular and DNA health. The innovative formula exceeds standard UV protection, guarding against UVA, UVB, damaging infrared rays, and blue light. Offering wide-ranging protection bolsters your skin's restorative abilities, promoting a healthier and more resilient complexion.
Designed to be fragrance-free and anti-comedogenic, Dermdefence SPF 50 ensures no skin irritation or pore clogging, making it an excellent choice for those with skin conditions like Acne, Rosacea, or Eczema. Its lightweight, non-greasy texture provides easy application and rapid absorption, without leaving a white cast.
Dermdefence SPF 50 also serves as a primer, providing a smooth finish for easy makeup application and ensuring a flawless look all day. Dermdefence SPF 50 provides unparalleled sun protection that will shield your skin and nurture its unique needs, maintaining its health and radiance.
Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 is a potent ingredient that offers comprehensive skin health and appearance benefits. Its role in energy production and its antioxidant and anti-aging properties make it invaluable for photoprotection, anti-aging, and overall skin vitality. Its incorporation into DermExcel sunscreen represents a holistic approach to skin health, addressing protective and restorative needs.
Physiological Impact
- Skin Barrier Enhancement: CoQ10 contributes to the strength and health of the skin barrier, improving its ability to retain moisture and protect against external irritants and pollutants.
- Skin Repair and Regeneration: It supports the skin's natural ability to repair itself and regenerate, maintaining a healthy, youthful appearance. This is particularly beneficial in mature skin, where natural levels of CoQ10 may be depleted.
Pharmacological Advantages
- Anti-Aging Effects: CoQ10's antioxidant properties contribute to its anti-aging effects. By reducing oxidative stress, it helps to minimize the visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines.
- Photoprotection: It enhances the skin's defense against photoaging caused by exposure to UV rays. CoQ10 helps to mitigate the degradation of collagen and elastin, proteins essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
Biochemical Benefits
- Cellular Energy Production: CoQ10 plays a crucial role in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, which is essential for the production of ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell. This function is vital for maintaining the health and vitality of skin cells.
- Antioxidant Properties: It acts as a lipophilic antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and preventing oxidative damage to cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. This is particularly important in the skin, which is frequently exposed to oxidative stress from environmental factors like UV radiation.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
Broad Spectrum Filters
Tinosorb® M and Tinosorb® S represent sophisticated advancements in sun protection technology.
Tinosorb® M
- Biochemical Action: A unique UV filter due to its ability to function through absorption, reflection, and scattering of UV rays.
- Physiological Impact: The triple-action mechanism of Tinosorb® M offers comprehensive sun protection. By mitigating the penetration of both UVA and UVB rays, it significantly reduces the risk of DNA damage, photoaging, and carcinogenesis. Its ability to remain on the skin's surface reduces systemic exposure, making it a safer option with minimal potential for irritation or allergic reactions.
Tinosorb® S
- Biochemical Action: A broad-spectrum UV filter with a molecular structure that effectively absorbs both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, it enhances the photostability of other UV filters, making the sunscreen formulation more effective over time.
- Physiological Impact: By providing extensive UVA and UVB protection, Tinosorb® S plays a crucial role in preventing short-term sun damage like sunburn and long-term risks such as skin aging and skin cancer. Its photostability ensures sustained protection during sun exposure, and its compatibility with other UV filters means it can be used to formulate sunscreens that are both effective and suitable for sensitive skin.
Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is a fundamental aspect of skin care and preventive dermatology. It's essential for reducing the risk of skin cancers and photoaging and maintaining overall skin health in the face of constant exposure to UV radiation.
Sunscreen is a vital skincare product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Two primary types of UV radiation affect the skin: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging and long-term skin damage, whereas UVB rays cause sunburn and play a key role in developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen products work by either absorbing, reflecting, or scattering sunlight. They contain chemical compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into a small amount of heat or physical compounds (like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) that act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV light away from the skin.
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF). SPF indicates how well the sunscreen protects against UVB rays. For example, an SPF of 30 means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn than without sunscreen. However, it's important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% UV rays.
Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can reduce the risk of skin cancer, prevent sunburn, and slow down the skin's aging process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Prevention of Sunburn: Sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. This reduces the immediate risk of skin damage and discomfort.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Regular use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, especially melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
- Prevention of Photoaging: Sunscreen also shields the skin from UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for photoaging, including wrinkles, leathery skin, and sunspots.
- Protection Against Photosensitivity: Sunscreen helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure for individuals with photosensitive skin conditions like lupus or rosacea.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: It aids in preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma, conditions exacerbated by sun exposure.
- General Skin Health: Sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health and integrity by protecting the skin from UV damage.
References
- Burnett, M. E., & Wang, S. Q. (2011). Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.
- Green, A. C., et al. (2011). Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine.
Testimonials
Fantastic products!! Been using them for 5 years now and never felt more confident in my own skin!! Nothing else I’ve ever tried came even close to these results. Awesomeness 😊🙌🏻
I have been using these products for 5 years now. There is simply nothing better. Noticed a change in my skin within 2 weeks.
Can already see a clear difference and it has only been 3 weeks.
This products really do work.
I started using Dermexcel products in December specifically to target my dark spots, and after just 4 weeks, I can already see a massive improvement. My skin looks healthier, brighter, and has a beautiful glow. My dark spots have slightly faded, and I’ve also noticed that my pores look more refined.
I’m genuinely impressed with how effective these products are, especially in such a short time. Definitely worth it, and I’m excited to see even more results with continued use!
Fantastic products and my dermal diagnosis was spot on
My skin looks and feels so good. I've been using the products for 4 years now and have never looked back. I'm 34 and grateful for such a good range of products to help with anti-aging.