The Science Behind Sleep-Deprived Skin
Discover how sleep deprivation affects your skin's health and appearance. Learn the science behind sleep-deprived skin, its symptoms, and how to rejuvenate your complexion with expert tips and advice. Get your glow back!

You can almost always tell when a person is sleep-deprived, as it shows immediately in their skin, mood, and overall health.
Our bodies depend on a good night’s sleep for rest and recovery from the day's stressors. During eight hours of sleep, our bodies go through three distinct stages that contribute to our overall well-being and aid in the nightly restoration of our skin.
Without regular, quality sleep, your skin’s ability to repair and rejuvenate itself is impaired. You may notice an increase in fine lines, uneven pigmentation, inflammation, and reduced elasticity in your skin.
Simply put, your lack of sleep may contribute to your breakouts or make you look older than your actual years.

Your pituitary gland produces somatotropin, the human growth hormone, during the first three hours of sleep. However, if you don't get adequate rest, you may not be producing enough of it.
This hormone helps to repair damaged skin cells and contributes to the maintenance of youthful and healthy skin. Without somatotropin, the daily breakdown in your skin doesn’t get a chance to repair overnight. Over time this can lead to more visible signs of aging.
Inadequate somatotropin further accelerates the aging process by breaking down collagen and elastic tissue, causing loose skin and wrinkles to develop.

During the middle two hours of sleep, your levels of melatonin increase. Melatonin is a hormone responsible for regulating your circadian rhythm (sleep/wake patterns). It acts as an antioxidant that helps protect the skin from free radicals – unstable atoms that cause illness and aging.

Poor oxygen-rich blood circulation to your skin leads to dull, lifeless skin. You lose your rosy cheeks.

- Get some rest. The first thing to do is create a bedtime routine and stick to it. If you decide to hit the pillow at 10 p.m., go to bed every night at that hour. Strive for 7 to 9 hours of sleep every night.
- Elevate your head with an extra pillow or bed wedge. This reduces snoring, acid reflux, and nasal drip—all of which can limit the quality of your sleep and affect the appearance of your skin.
- Wash your face to remove oils, dirt, and makeup before bedtime.
- Apply skin-repairing serums at night. Reparative and restorative active ingredients are much more effective when applied at night. While you sleep, your skin can focus on repairing itself since it isn’t defending itself from the sun and free radicals (harmful environmental molecules). Blood flow is also more consistent, and this helps your skin benefit from the tissue-repairing ingredients in your treatment products.
- Apply Time Freeze eye serum or Dark Circle eye serum about 15 minutes before turning in for the night. This gives them a chance to work rather than merely rubbing off on the pillowcase.

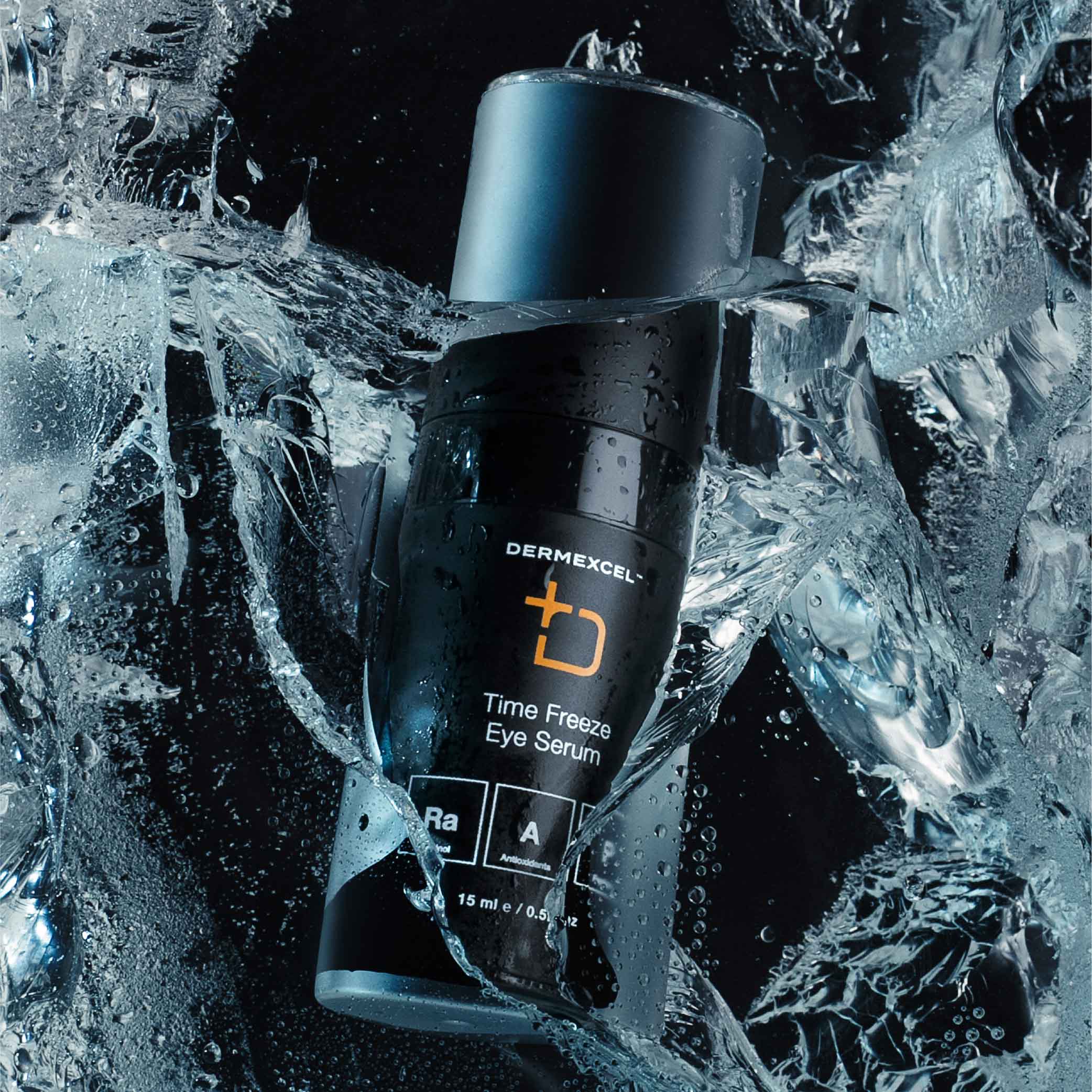
TIME FREEZE EYE SERUM
Time Freeze eye serum reduces the depth of wrinkles around the eyes caused by the contraction of facial expression muscles. It visibly improves the skin's elasticity by building up collagen and decreasing wrinkle progression.
This formulation contains a special blend of active ingredients that firms the eye contour and strengthens vessels and tissues around the eyes.
It stimulates the production of collagen and elastin, which restore the strength of the vascular wall, and it also promotes the re-densification of the skin.
Time Freeze Eye serum transforms tired, dull, aging skin into a glowing and youthful complexion.
____
DARK CIRCLE EYE SERUM
A powerful formulation that targets dark circles, puffiness, and signs of aging to deliver radiant and energized eyes.
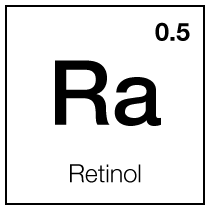
Dark circle eye serum contains 1% Vitamin K1 and 0.15% Vitamin A (Retinol) entrapped in a polymeric delivery system that gradually releases the entrapped vitamins to penetrate the epidermis and the dermis.
Combining active ingredients improves microvascular integrity and microcirculation, reduces swelling, and stimulates the skin’s firmness.
This has a dual effect of reducing dark circles and spider veins and shrinking puffy areas, resulting in smooth and vibrant skin.
Treatment for sleep deprived eyes






Pay interest-free installments from R 189.13 with various payment gateways selected at checkout.
SIZE: 15 mL

Anti-Aging

Antioxidant

Moisturizing

Firming

↑ Elasticity
A potent firming formulation specifically designed to target lines, wrinkles, puffiness, and sagging skin beneath the eyes. The serum tightens the skin upon application and has a long-lasting impact, significantly contributing to an uplifted and defined face contour.
Its power derives from key ingredients such as Argireline known for its ability to reduce the appearance of wrinkles by inhibiting neural signals that cause facial muscles to tense, indirectly leading to a smoother skin surface. Bioskinup Contour™, a blend of botanical extracts, offers anti-edema properties that mitigate puffiness.
Retinol, specifically in the form of Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate, a less irritating retinoid, facilitates cellular renewal, aiding the skin in appearing firm and reducing the visibility of age-related changes. Furthermore, antioxidants, such as Tocopherol (Vitamin E), guard against harmful free radicals, fostering the resilience of the skin.
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8: The Innovative Peptide in Anti-Aging Dermatology
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 is a testament to the advancements in peptide technology in dermatology. Its ability to reduce facial muscle contractions non-invasively positions it as an essential ingredient in anti-aging skincare.
Biochemical Mechanism
Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 functions by inhibiting the neurotransmitters that trigger muscle contractions. This action reduces the intensity of wrinkle-causing facial expressions, leading to a visible decrease in fine lines and wrinkles. It mimics the N-terminal end of SNAP-25, competing with this natural protein for a position in the SNARE complex, thereby destabilizing it. As a result, neurotransmitter release is diminished, and facial muscle contractions are softened.
Physiological Effects
- Neurotransmitter Inhibition: Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 works by inhibiting neurotransmitter release. This leads to reduced facial muscle contraction, a mechanism similar to Botox but less invasive.
- Reduction of Expression Lines: Helps to reduce the appearance of expression lines, particularly around the forehead and eyes, by limiting muscle contraction.
- Improvement in Skin Texture: Regular use can lead to smoother skin texture and a reduction in the depth and severity of wrinkles.
Special Benefits
Clinical Efficacy - Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 in reducing wrinkle depth. A study published in the "International Journal of Cosmetic Science" reported that a cream containing 10% Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 reduced wrinkles by 30% over 30 days (Blanes-Mira et al., 2002).
References
- Blanes-Mira, C., et al. (2002). A synthetic hexapeptide (Argireline) with antiwrinkle activity. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Wang, Y., et al. (2013). The anti-wrinkle efficacy of Argireline. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy.
- Ruiz, M. A., et al. (2007). New cosmetic formulations containing Argireline. Journal of Cosmetic Science.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
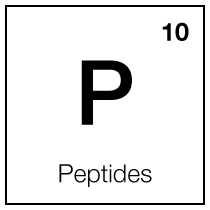
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids with a wide range of biological functions and skin benefits. They are essentially small fragments of proteins, which are fundamental components of all living cells, including collagen and elastin in the skin.
In skincare, peptides are known for enhancing skin repair and rejuvenation. They function as signaling molecules, instructing cells to perform specific tasks such as producing collagen and elastin, vital for maintaining the skin's firmness and elasticity. This makes peptides especially beneficial in anti-aging products, as they can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Research has shown that certain peptides can improve skin barrier function, increase hydration, and soothe skin inflammation. This makes them suitable for products targeting dry, sensitive, or inflamed skin.
Peptides, with their diverse functions in promoting collagen production, strengthening the skin barrier, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory actions, are pivotal in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly in anti-aging, sensitive skin care, and wound healing applications.
Physiological Effects
- Collagen Production: Certain peptides, known as signal peptides, stimulate collagen production in the skin, enhancing skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Barrier Strengthening: Peptides can strengthen the skin barrier, improve hydration, and protect against environmental damage.
- Wound Healing: Some peptides play a role in the skin's natural healing process, aiding tissue repair and regeneration.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Certain peptides have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to soothe and calm irritated skin.
- Antimicrobial Action: Some peptides possess antimicrobial properties, potentially helping to manage acne and other skin infections.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Peptides can stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity.
- Sensitive Skin Conditions: Peptides are beneficial for sensitive or inflamed skin due to their soothing properties.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Antimicrobial peptides can be effective in acne treatment formulations.
- Wound Care and Repair: Peptides improve wound healing and reduce scarring.
References
- Gorouhi, F., & Maibach, H. I. (2009). Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Schagen, S. K. (2012). Topical peptide treatments with effective anti-aging results. Cosmetics.
- Varani, J., et al. (2001). Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Retinoic acid analogue
Retinoic acid, often referred to as tretinoin in its pharmaceutical form, is the active form of Vitamin A. It is widely recognized for its powerful effects in dermatology and skin care, particularly in treating acne and signs of skin aging.
Retinoic acid works at the cellular level to modify gene expression and affect cell growth. In treating acne, it promotes the turnover of skin cells, reducing the likelihood of pore-clogging and helping to clear existing breakouts. Additionally, it decreases the cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells, further preventing the formation of comedones.
Retinoic acid's ability to stimulate collagen production is a key benefit in anti-aging skincare. This leads to a reduction in fine lines and wrinkles and an improvement in overall skin texture and tone. It also aids skin discoloration and hyperpigmentation by accelerating cell turnover, bringing new skin cells to the surface faster, and shedding pigmented and damaged cells.
Despite its benefits, retinoic acid can irritate the skin, causing side effects like redness, dryness, and peeling, especially during the initial period of use. Its potency means it is generally available by prescription and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR) is a newer, esterified form of retinoic acid. Unlike cosmetic retinol, HPR binds directly to the retinoid receptors of the skin cells without needing conversion. This direct binding allows it to deliver similar benefits to retinoic acid, such as stimulating collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and reducing signs of aging, but with a lower risk of irritation.
HPR is considered more gentle and less irritating than traditional retinoic acid while offering comparable benefits. With HPR, everyone has access to the benefits of prescription retinoids without the risk of side effects.
Physiological Effects
- Cell Turnover and Renewal: HPR promotes rapid cell turnover, aiding in the exfoliation of dead skin cells and generating new cells.
- Skin Texture: Promoting cell renewal improves skin texture and addresses issues like roughness and dullness.
- Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improving skin elasticity.
- Acne Treatment: Effective in treating acne by unclogging pores and reducing the size of sebaceous glands, it diminishes both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions.
- Pigmentation: It can reduce hyperpigmentation by accelerating the turnover of hyperpigmented skin cells and inhibiting melanin production.
- Photoaging: Effective in treating signs of photoaging, reversing some of the damage caused by UV radiation.
Special Benefits
- Retinoid Receptor Activity: HPR, an ester of retinoic acid, binds directly to retinoid receptors in the skin, enabling it to work without needing to be converted into retinoic acid.
- Lower Irritation: Typically, it causes less irritation than retinoic acid, making it more suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Collagen Stimulation and Anti-Aging: Like retinoic acid, HPR helps in stimulating collagen production and has anti-aging properties.
- Acne and Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats acne and reduces hyperpigmentation, often with fewer side effects than retinoic acid.
- Stability and Penetration: HPR is more stable and lipid-soluble, so it penetrates the skin more effectively and is less prone to degradation.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., ... & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Fisher, G. J., Wang, Z. Q., Datta, S. C., Varani, J., Kang, S., & Voorhees, J. J. (1996). Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. New England Journal of Medicine, 337(20), 1419-1428.
- Truchuelo, M. T., Jiménez, N., Jaén, P. (2018). Assessment of the efficacy of a new complex-based retinoic acid and retinol in a 3-month study using objective methods and skin biomarker analysis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 17(3), 347-354.
- Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging.
- Randhawa, M., et al. (2015). Hydroxypinacolone retinoate: a new retinoid and its use in dermatology. Skin Therapy Letter.
Bioskinup Contour
Bioskinup Contour 3R demonstrates a comprehensive mechanism of action targeting periorbital puffiness and dark circles. It stimulates collagen and elastin production, enhancing skin firmness and vascular wall resistance.
Clinical studies highlight its ability to maintain skin health under UV radiation, suggesting adaptogenic properties. In vivo evaluations reveal significant improvements in skin and ocular acceptability, with reductions in puffiness, dark circles, and under-eye bags. Instrumental assessments confirm its efficacy in enhancing microcirculation and skin tone, validating its dermatocosmetic benefits for the eye area.






Pay interest-free installments from R 169.56 with various payment gateways selected at checkout.
SIZE: 15 mL

Anti-Aging

Firming

Even Skin Tone

↑ Elasticity

↓ inflammation
A high-potency solution targeting aging signs in the eye area, particularly dark circles. The serum hinges on medical-grade Vitamin K1 or Phylloquinone, noted in dermatological literature for its role in the body's blood clotting process, which can assist in fading the appearance of dark circles.
Additionally, Bioskinup Contour™, an innovative blend of botanical extracts, helps reduce puffiness and fatigue signs. The inclusion of Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate, a gentle retinoid, promotes skin cell turnover, mitigating the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
In synergy, antioxidants, notably Tocopherol (Vitamin E), provide a protective shield against environmental stressors, while peptides, the building blocks of proteins, support the skin's natural structure, aiding in maintaining the skin's firmness and elasticity.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
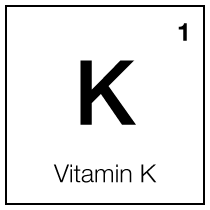
Vitamin K1
Vitamin K1, known as phylloquinone, is primarily recognized for its crucial role in blood coagulation. Beyond its well-known effects on blood clotting, recent research has highlighted its potential benefits in skin care, particularly in managing bruising and dark circles under the eyes and improving skin elasticity. Its mechanisms of action involve regulating blood clotting and reducing blood leakage into the skin and soft tissues. This property makes it particularly useful in topical treatments to minimize bruising and under-eye dark circles, often caused by fragile capillaries leaking small amounts of blood.
Studies have suggested that when applied topically, Vitamin K1 can help reduce the severity and duration of bruising after laser procedures or surgical treatments. It is believed to aid in the body's process of reabsorbing blood near the skin's surface, thereby reducing the appearance of bruises.
Physiological Effects
Blood Clotting and Bruising: Vitamin K1 is critical in blood clotting. It helps reduce the appearance of bruises on the skin by aiding the body's natural healing process in resolving blood clots.
- Improving Skin Elasticity: It is believed to help improve skin elasticity and may reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin K1 can assist in the skin's healing process, although its effectiveness in wound healing needs further research.
- Under-Eye Circles: The topical application of Vitamin K1 is thought to reduce the appearance of dark circles under the eyes by strengthening capillary walls and reducing the visibility of blood vessels beneath the skin.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Postoperative Bruising: It is often used in topical creams to reduce bruising following cosmetic skin procedures.
- Dark Circles Under the Eyes: Creams containing Vitamin K1 diminish the appearance of dark circles caused by visible blood vessels or hyperpigmentation.
- Skin Aging: Its potential anti-aging properties might benefit products targeting aging skin concerns.
References
- Shah, N. S., et al. (2002). The effects of topical vitamin K on bruising after laser treatment. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Cohen, J. L., & Bhatia, A. C. (2009). The role of topical vitamin K oxide gel in the resolution of postprocedural purpura. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
- AlQdah, T. (2021). Vitamin K in Dermatology. Dermatology Practical & Conceptual.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A, a fat-soluble vitamin, is critical in maintaining healthy skin, vision, and overall immune function. In dermatology, it is particularly celebrated for its potent effects on skin health and its use in treating a variety of skin conditions.
There are two primary forms of vitamin A: retinoids (including retinol), which are found in animal products, and carotenoids, which are present in plants. Retinoids are biologically active and are used both topically and systemically in dermatology. Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin and adapalene, are widely used in treating acne and photoaging because they regulate skin cell turnover and boost collagen production, resulting in clearer and smoother skin.
Vitamin A's role in promoting cell turnover helps to unclog pores and reduce the severity of acne. It also aids in diminishing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, making it a key ingredient in many anti-aging skincare products. Additionally, vitamin A can help normalize this process in the treatment of psoriasis, a condition characterized by excessive skin cell production.
Vitamin A also possesses antioxidant properties, which help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Physiological Effects
- Cellular Turnover: It stimulates cell turnover in the skin. This means it helps shed old skin cells and replace them with new ones, improving skin texture and tone.
- Collagen Production: It aids in collagen production, essential for maintaining skin elasticity and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Regulation of Sebum Production: Help regulate sebum production, which is beneficial for acne-prone skin.
- Pigmentation: It assists in regulating skin pigmentation, helping to even out skin tone and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Photoprotection: Antioxidant properties that protect the skin from damage caused by UV rays.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne: Vitamin A derivatives, like retinoids, are highly effective in treating acne by preventing clogged pores and reducing inflammation.
- Aging Skin: Topical retinoids reduce signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines, by boosting collagen production.
- Psoriasis: Vitamin A can help manage psoriasis by normalizing skin cell growth.
- Hyperpigmentation: It helps treat hyperpigmentation and melasma by accelerating skin cell turnover.
- Sun Damage: Vitamin A's antioxidant properties can help to some extent in repairing and preventing sun damage.
References
- Mukherjee, S., Date, A., Patravale, V., Korting, H. C., Roeder, A., & Weindl, G. (2006). Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 1(4), 327–348.
- Kang, S., et al. (2005). Topical Retinoids. In: Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine.
- Kafi, R., et al. (2007). Improvement of Naturally Aged Skin With Vitamin A (Retinol). Archives of Dermatology.
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids with a wide range of biological functions and skin benefits. They are essentially small fragments of proteins, which are fundamental components of all living cells, including collagen and elastin in the skin.
In skincare, peptides are known for enhancing skin repair and rejuvenation. They function as signaling molecules, instructing cells to perform specific tasks such as producing collagen and elastin, vital for maintaining the skin's firmness and elasticity. This makes peptides especially beneficial in anti-aging products, as they can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Research has shown that certain peptides can improve skin barrier function, increase hydration, and soothe skin inflammation. This makes them suitable for products targeting dry, sensitive, or inflamed skin.
Peptides, with their diverse functions in promoting collagen production, strengthening the skin barrier, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory actions, are pivotal in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly in anti-aging, sensitive skin care, and wound healing applications.
Physiological Effects
- Collagen Production: Certain peptides, known as signal peptides, stimulate collagen production in the skin, enhancing skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Barrier Strengthening: Peptides can strengthen the skin barrier, improve hydration, and protect against environmental damage.
- Wound Healing: Some peptides play a role in the skin's natural healing process, aiding tissue repair and regeneration.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Certain peptides have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to soothe and calm irritated skin.
- Antimicrobial Action: Some peptides possess antimicrobial properties, potentially helping to manage acne and other skin infections.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Peptides can stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity.
- Sensitive Skin Conditions: Peptides are beneficial for sensitive or inflamed skin due to their soothing properties.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Antimicrobial peptides can be effective in acne treatment formulations.
- Wound Care and Repair: Peptides improve wound healing and reduce scarring.
References
- Gorouhi, F., & Maibach, H. I. (2009). Role of topical peptides in preventing or treating aged skin. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Schagen, S. K. (2012). Topical peptide treatments with effective anti-aging results. Cosmetics.
- Varani, J., et al. (2001). Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Bioskinup Contour
Bioskinup Contour 3R demonstrates a comprehensive mechanism of action targeting periorbital puffiness and dark circles. It stimulates collagen and elastin production, enhancing skin firmness and vascular wall resistance.
Clinical studies highlight its ability to maintain skin health under UV radiation, suggesting adaptogenic properties. In vivo evaluations reveal significant improvements in skin and ocular acceptability, with reductions in puffiness, dark circles, and under-eye bags. Instrumental assessments confirm its efficacy in enhancing microcirculation and skin tone, validating its dermatocosmetic benefits for the eye area.